Volume 12, Number 10—October 2006
Research
Active Cytomegalovirus Infection in Patients with Septic Shock
Figure
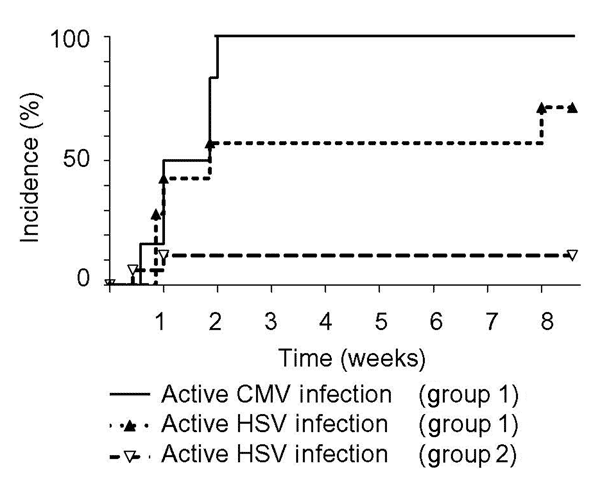
Figure. First detection of cytomegalovirus (CMV) and herpes simplex virus (HSV) reactivation after onset of septic shock. Incidence of active CMV and HSV infection is shown for patients with active CMV infection (group 1; n = 8) and without active CMV infection (group 2; n = 17). CMV reactivation occurred during the first 2 weeks after onset of septic shock (median 7 days) and was associated with HSV reactivation, which occurred during the same period. The incidence of active HSV infection was different between groups 1 and 2 (75% vs 12%; p = 0.004). Active CMV infection was detected first by CMV pp65 antigenemia; active HSV infection was detected by virus isolation of bronchial aspirates.
Page created: November 10, 2011
Page updated: November 10, 2011
Page reviewed: November 10, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.