Volume 12, Number 11—November 2006
Dispatch
Human Parainfluenza Type 4 Infections, Canada
Figure 2
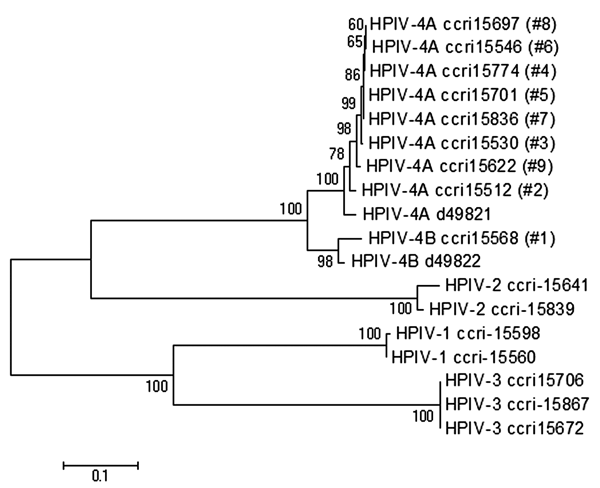
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis based on fusion (F) gene nucleotide sequences from clinical and reference human parainfluenza virus (HPIV) strains. The tree was built by using distance method and the neighbor-joining algorithm with Kimura 2 parameters. The topologic accuracy of the tree was evaluated by using 500 bootstrap replicates. Strains isolated at the Research Center in Infectious Diseases (Quebec, Canada) are indicated by a specific identification number (ccri) followed by the patient number in parentheses. Public sequences for HPIV-4A (GenBank accession no. d49821) and HPIV-4B (GenBank accession no. d49822) strains are also indicated in the tree.
Page created: October 14, 2011
Page updated: October 14, 2011
Page reviewed: October 14, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.