Volume 12, Number 11—November 2006
Dispatch
Identical Genotype B3 Sequences from Measles Patients in 4 Countries, 2005
Abstract
Surveillance of measles virus detected an epidemiologic link between a refugee from Kenya and a Dutch tourist in New Jersey, USA. Identical genotype B3 sequences from patients with contemporaneous cases in the United States, Canada, and Mexico in November and December 2005 indicate that Kenya was likely to have been the common source of virus.
Identification of measles virus genotypes is a valuable tool for epidemiologic investigations and evaluation of control activities in countries that have eliminated indigenous measles. Many of the 23 recognized genotypes of measles are associated with countries or regions with endemic measles (1). Measles genotypes in clade B (genotypes B1, B2, B3) are associated with endemic circulation of measles in various countries in sub-Saharan Africa (2). The prototype clade B viruses were isolated in 1983 in Cameroon (B1) and in 1984 in Gabon (B2). Hanses et al. (3) proposed a new genotype, B3, after characterization of several viruses collected in 1997 and 1998 in Ghana and Nigeria. Sequencing studies of additional viruses from Africa demonstrated that the proposed subdivision of the B3 viruses into subgroups B3.1 and B3.2 was epidemiologically useful for describing 2 distinct clusters of contemporary B3 viruses (4,5).
Because measles is highly infectious, international travel originating from measles-endemic areas can result in sporadic cases of measles in countries that have eliminated indigenous transmission. International visitors may infect other travelers while moving through transportation hubs or tourist areas; such cases would not be detected unless the traveler sought medical attention or additional cases were detected. Thus, in many of these instances, the source of virus is unknown. We describe the contribution of global surveillance for measles virus genotypes in identifying a common source of virus among contemporaneous cases identified in the United States, Canada, Mexico, and the Netherlands.
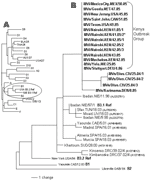
On November 9, 2005, a 17-year-old man who arrived at the airport in Newark, New Jersey, United States, had symptoms consistent with measles. The man was part of a group of 148 refugees from the Eastleigh community in Nairobi, Kenya, who arrived in the United States from November 3 through 15. Genotype B3 (subgroup B3.1) was identified from virus samples from this patient; the sequence was identical to sequences from measles viruses collected in Nairobi and Machakos, Kenya, in October 2005 (Figure). All but 1 of the 6 viruses collected from Nairobi (Figure, MVi/Nairobi.KEN.xx.05) were from patients from the Eastleigh area of Nairobi, where an outbreak of measles had been reported in the Somali and Ethiopian communities (6).
Also in November 2005, a single case of measles was reported in the Netherlands. This patient had visited New York City, returned to the Netherlands on November 15, noted a rash on November 23, and was hospitalized with pneumonia and fever on November 24. The initial investigation focused on potential settings where exposure may have occurred in New York City. The source of infection was traced to an unrecognized exposure to the patient in New Jersey only after analysis of the Netherlands viral sequence demonstrated complete identity with the New Jersey genotype B3 virus. The possibility of an epidemiologic link between the 2 cases led to the discovery that the Dutch visitor had arrived at the Newark airport on November 9 and waited in the arrival area for 1 h, along with the group of refugees from Nairobi.
Subsequently, genotype B3 was identified from patients who had had measles during December 2005 in Texas, Canada, and Mexico. In Texas, during the first 2 weeks of December, 3 cases of measles were reported in members of a family from Houston. The patients had flown directly from Houston to the resort area of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico, where they stayed from November 22 through 27. In Mexico, health authorities reported 5 cases of measles beginning on December 12 among baggage handlers and other airport workers at the Mexico City airport. In New Brunswick, Canada, a patient developed a rash on December 19.
Although the earlier cases in New Jersey and in the Netherlands could be traced directly to the outbreak in Kenya, the sources of the cases in Texas, Canada, and Mexico were unknown. However, the sequences from Texas, Canada, and Mexico were identical to the sequences directly linked to the outbreak in Kenya (Figure). Measles viruses in the same chain of transmission have identical sequences (7,8), which indicates that the source of the virus for the cases in Texas, Mexico, and Canada was likely to have been the outbreak in Kenya.
Virus transmission may have occurred through contact with international travelers in airports or during transit because epidemiologic investigations did not detect other measles cases in Cabo San Lucas or Texas. The exception to possible air travel–related exposure was the single case that occurred in Canada. This patient had traveled by car, although investigations found no measles cases in the areas visited: Bangor, Maine (December 2); Boston, Massachusetts (December 3–6); and Portsmouth, New Hampshire (December 6). Two refugees from Eastleigh settled in a state visited by the Canadian patient. They entered Massachusetts on November 10, 2005, and by 21 days after arrival, measles had not developed. However, a measles outbreak was detected in southern Germany in January 2006 (9), and the viral sequence matched that of the Kenya outbreak virus (Figure; MVs/Stuttgart.DEU/4.06), which indicates that the source of this outbreak was also likely to have been Kenya. Therefore, B3 viruses with identical sequences could have been introduced into Texas, Mexico, or Canada by travelers infected with B3 virus in Europe.
Although genotype B3 has been the most frequently detected measles genotype in western and central Africa (4,10–12), ours is the first report of the detection of genotype B3 in Kenya. Moreover, the sequence from a virus isolated in Nigeria in June 2005 (Figure; MVs/Yola.NIE/25.05) was identical to the sequences in the Kenya outbreak group. Although a link has not been established between Nigeria and Kenya, a survey of measles genotypes in Kenya in 2002 detected only genotype D4 viruses (13). Sequences of viruses isolated during 2004 and 2005 from Côte d'Ivoire and Benin (this study) were included in our analysis (Figure) because these B3 sequences represent closely related viruses from western Africa.
The analysis and dissemination of viral sequences from measles cases led to the identification of an unrecognized epidemiologic link at an airport and linked sporadic cases in 4 countries that do not have endemic measles to an ongoing outbreak in Kenya. Investigators in the field need to collect adequate specimens for virus isolation. Timely communication of sequence data among epidemiologists and microbiologists is critical for identifying possible links among sporadic cases of measles. The potential for rapid transmission of measles during brief encounters with international travelers underscores the importance of global surveillance of measles virus.
Ms Rota is a public health advisor and laboratory coordinator in the Measles, Mumps, Rubella, and Herpesviruses Laboratory Branch at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Her interests include international public health of infectious diseases, primarily vaccine-preventable diseases, and the molecular epidemiology of measles virus.
Acknowledgment
We gratefully acknowledge the following persons for support with the investigations: Cathy Cuomo-Cecere, Marsha McGowan, Zofia Lesczyniecka, Jim Oleske, Polly Thomas, Tong Wey, Nancy Borsuk, Wendy Sessions, Tim Kram, Christine Teel, Beverly Howe, Mary Jane Lowrey, Shola Adeleye, Steve Long, Anthony Eshofonie, Salma Khuwaja, Debo Awosika-Olumo, Cindy Kilborn, Sherry Jin, Heather Martin, and Teresa York. We also thank Traore Ibrahima, Herve Kadjo, Tieoulou Leontine, Koffi Signo Paul, Agnes Langat, Mary Njeri, Peter Maritim, Ronald Seguya, Theopista Kabaliisa, Martin Khargi, Esther Mooi-Kokenberg, and Henny Peltenburg.
References
- World Health Organization. New genotype of measles virus and update on global distribution of measles genotypes. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2005;80:347–51.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Riddell M, Rota JS, Rota PA. Review of the temporal and geographical distribution of measles virus genotypes in the prevaccine and postvaccine eras. Virol J. 2005;2:87 [cited 2006 Aug 13]. Available from http://www.virologyj.com/content/2/1/87
- Hanses F, Truong AT, Ammerlaan W, Ikusika O, Adu F, Oyefolu AO, Molecular epidemiology of Nigerian and Ghanaian measles virus isolates reveals a genotype circulating widely in western and central Africa. J Gen Virol. 1999;80:871–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kouomou DW, Nerrienet E, Mfoupouendoun J, Tene G, Whittle H, Wild TF. Measles virus strains circulating in central and west Africa: geographical distribution of two B3 genotypes. J Med Virol. 2002;68:433–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gouandjika-Vasilache I, Waku-Kouomou D, Ménard D, Beyrand C, Guye F, Ngoay-Kossy JC, Cocirculation of measles virus genotype B2 and B3.1 in Central African Republic during the 2000 measles epidemic. J Med Virol. 2006;78:964–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sharif SK. Measles, Refugee children—Kenya (Nairobi). ProMed. October 27, 2005 [cited 2006 Aug 17]. Available from http://www.promedmail.org, archive no.: 20051027.3131.
- Oliveira MI, Rota PA, Curti SP, Figueiredo CA, Afonso AMS, Theobaldo M, Genetic homogeneity of measles viruses associated with a measles outbreak, São Paulo, Brazil, 1997. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:808–13.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Parker AA, Staggs W, Dayan GH, Ortega-Sanchez IR, Rota PA, Lowe L, Implications of a 2005 measles outbreak in Indiana for sustained elimination of measles in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:447–55. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Eurosurveillance. Outbreaks of measles in Germany, 2006. Euro Surveill Wkly Rel. 2006;11(3) [cited 2006 Aug 13]. Available from http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ew/2006/060323.asp
- El Mubarak HS, van de Bildt MWG, Mustafa OA, Vos HW, Mukhtar MM, Ibrahim SA, Genetic characterization of wild-type measles viruses circulating in suburban Khartoum, 1997–2000. J Gen Virol. 2002;83:1437–43.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Djebbi A, Bahri O, Mokhtariazad T, Alkhatib M, Yahia AB, Rezig D, Identification of measles virus genotypes from recent outbreaks in countries from the Eastern Mediterranean Region. J Clin Virol. 2005;34:1–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mosquera MM, Ory F, Echevarría JE; The Network of Laboratories in the Spanish National Measles Elimination Plan. Measles virus genotype circulation in Spain after implementation of the National Measles Elimination Plan 2001–2003. J Med Virol. 2005;75:137–46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mbugua FM, Okoth FA, Gray M, Kamau T, Kalu A, Eggers R, Molecular epidemiology of measles virus in Kenya. J Med Virol. 2003;71:599–604. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figure
Cite This ArticleTable of Contents – Volume 12, Number 11—November 2006
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Jennifer Rota; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Mailstop C22, 1600 Clifton Rd NE, Atlanta, GA 30333, USA
Top