Volume 12, Number 6—June 2006
Dispatch
Mixed Cryptosporidium Infections and HIV
Figure
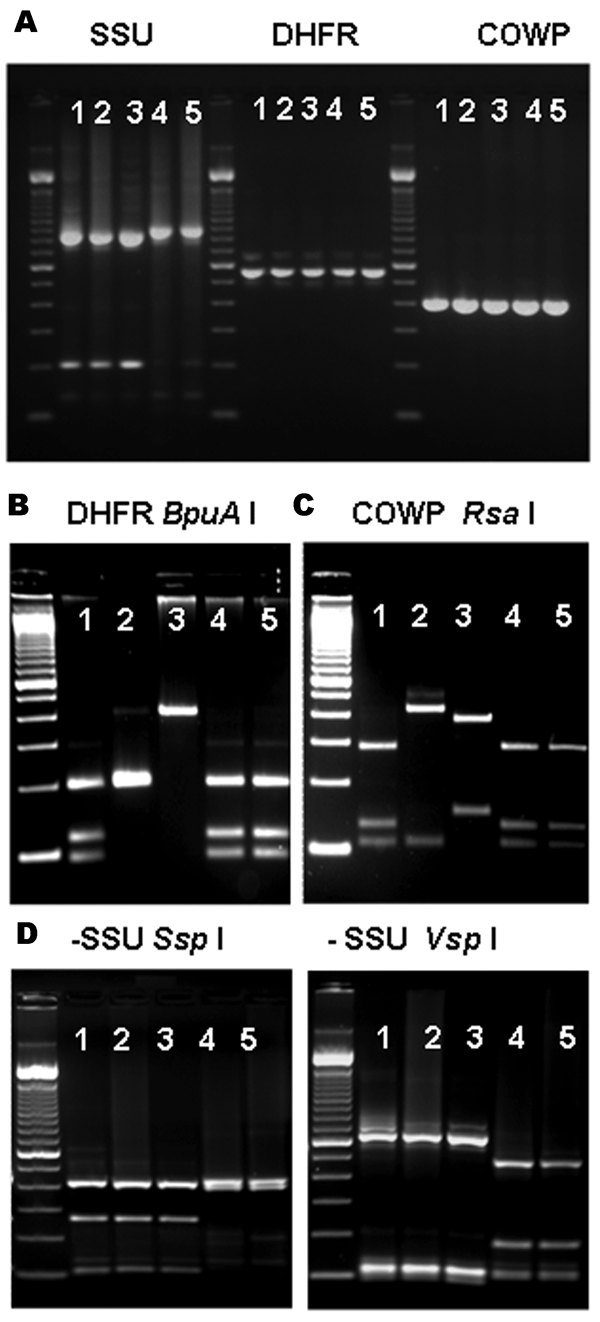
Figure. Multilocus polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) analysis of specimens previously identified as Cryptosporidium canis and C. felis. A) Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR-amplified products of specimens previously identified as C. canis (lanes 1–3) and C. felis (lanes 4 and 5) with molecular tools based on the small subunit (SSU) rRNA, dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), and Cryptosporidium oocyst wall protein (COWP). Molecular markers in all photos are 100-bp ladders. B) RFLP analysis of DHFR-based PCR amplification products using BpuA I restriction enzyme; lanes 1, 4, and 5 are C. hominis; lane 2 is C. parvum; and lane 3 is C. meleagridis. C) RFLP analysis of COWP-based PCR amplification products using Rsa I restriction enzyme; lanes 1, 4, and 5 are C. hominis; lane 2 is C. parvum; and lane 3 is C. meleagridis. D) RFLP analysis of the SSU-based PCR products using restriction enzymes Ssp I (left) and Vsp I (right); the combined patterns for lanes 1 to 3 correspond to C. canis and lanes 4 and 5 to C. felis.