Volume 13, Number 1—January 2007
Dispatch
Human Bocavirus Infection, People’s Republic of China
Figure
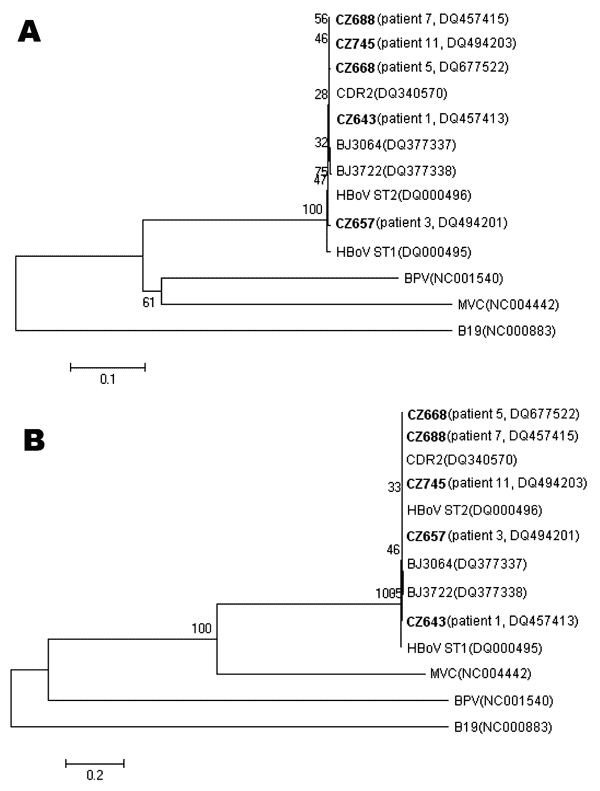
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of the complete VP1 nucleotide (A) and amino acid (B) sequences of human bocavirus (HBoV). Phylogenetic trees were constructed by the neighbor-joining method by using MEGA 3.1 (www.megasoftware.net), and bootstrap values were determined by 1,000 replicates. Viral sequences in boldface were generated from the present study, and other reference sequences were obtained from GenBank. Bootstrap values are shown at each branching point. The sequences generated from the present study were deposited in GenBank under accession nos. DQ457413, DQ457415, DQ494201, DQ494203, and DQ677522.
Page created: June 28, 2010
Page updated: April 05, 2012
Page reviewed: April 05, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.