Volume 13, Number 11—November 2007
Research
Epidemiologic and Virologic Investigation of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease, Southern Vietnam, 2005
Figure 2
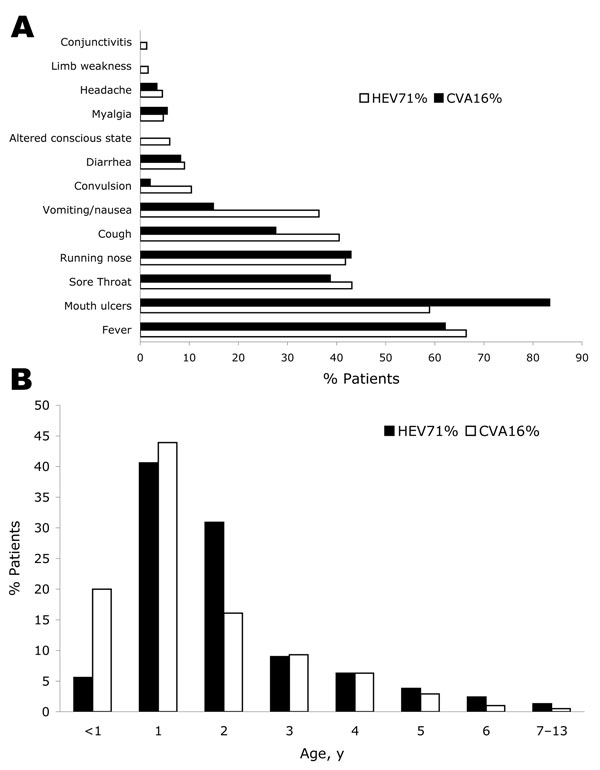
Figure 2. Clinical features of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) in children admitted to hospital in southern Vietnam during 2005. Features were associated with the isolation of coxsackievirus A16 (CVA16) (214 cases) or human enterovirus 71 (HEV71) (173 cases) from vesicle, throat swab, or stool specimens. A) Percentage distribution of clinical signs and symptoms among identified cases of HFMD. B) Percentage age distribution of patients with identified cases of HFMD.
Page created: July 06, 2010
Page updated: July 06, 2010
Page reviewed: July 06, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.