Volume 13, Number 12—December 2007
Letter
Distemper in a Dolphin
Figure
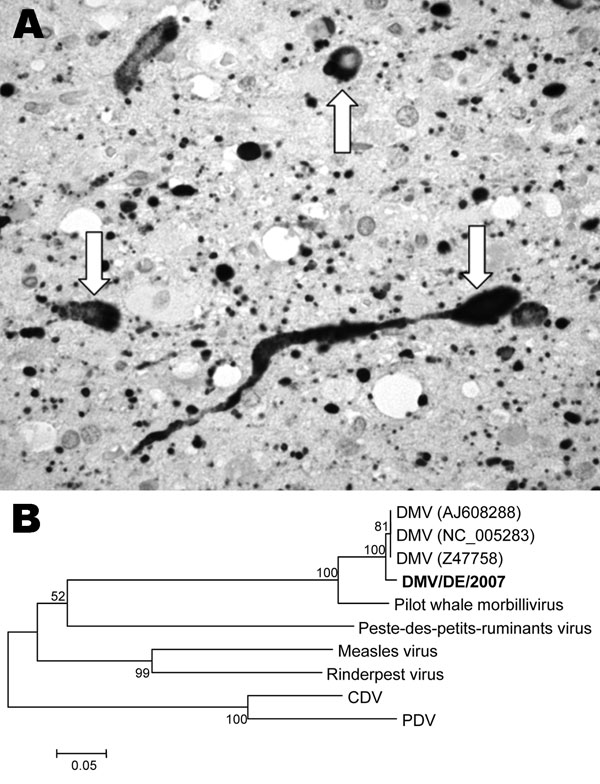
Figure. A) Immunohistologic demonstration of morbillivirus antigen in cytoplasm and nuclei of neurons (arrows) and glial cells in the brain of a white-beaked dolphin, using a monoclonal antibody (GenWay, San Diego, CA, USA) against nucleoprotein of canine distemper virus (CDV)/phocine distemper virus (PDV) visible as numerous black dots (magnification ×630). B) Unrooted neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree constructed by using 353 nt from the gene coding for the morbillivirus phosphoprotein. Alignments were calculated with ClustalX version 1.83 (http://bips.u-strasbourg.fr/fr/Documentation/ClustalX). Bootstrapping (values indicated in %) was performed with 1,000 replicates using MEGA 3.1 software (www.megasoftware.net/mega.html). The new isolate from this study is shown in boldface. The following sequences were included: dolphin morbillivirus (DMV) (GenBank accession nos. NC_005283, Z47758, AJ608288), pilot whale morbillivirus (AF200817), Peste-des-petits-ruminants virus (NC_006383), measles virus (NC_001498), Rinderpest virus (NC_006296), CDV (NC_001921), and PDV (D10371). Scale bar shows nucleotide substitutions per site.