Volume 13, Number 3—March 2007
Dispatch
Rapidly Fatal Acanthamoeba Encephalitis and Treatment of Cryoglobulinemia
Figure 2
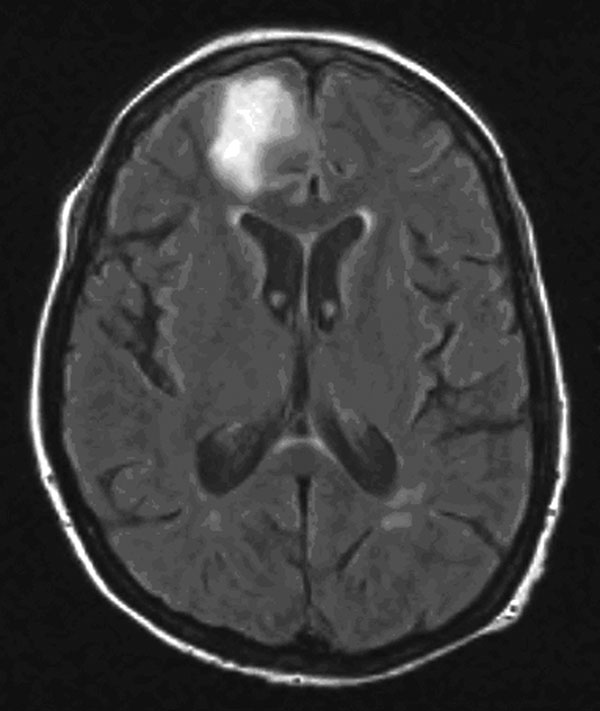
Figure 2. A) Cysts in a vessel wall (arrows) of the patient (hematoxylin and eosin stain, magnification ×250). Inset shows a cyst at higher magnification (hematoxylin and eosin stain, magnification ×800). B) Immunohistochemical staining with antibody to Acanthamoeba cysts within vessel walls (magnification ×250). C) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of PCR products for Acanthamoeba spp., Naegleria spp., and Balamuthia mandrillaris using JDP primers for a diagnostic small subunit rDNA fragment. M, molecular mass marker; Pat, patient; Neg, negative control; Pos, positive control.
Page created: June 29, 2010
Page updated: June 29, 2010
Page reviewed: June 29, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.