Volume 13, Number 3—March 2007
Dispatch
Detection of G12 Human Rotaviruses in Nepal
Figure 1
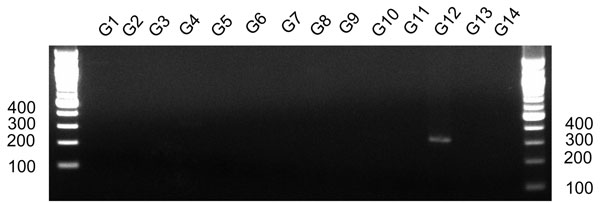
Figure 1. Detection after electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel of the PCR amplification product with a primer pair G12F and G12R. The prototype rotavirus strain for each G serotype was as follows; G1, Wa; G2, KUN; G3, MO; G4, ST3; G5 OSU; G6, NCDV; G7, PO-13; G8, MW33; G9, 95H115; G10, B223; G11, YM; G12, L26; G13, L338; and G14, FI23. The first and last lanes show molecular mass markers in basepairs.
Page created: June 29, 2010
Page updated: June 29, 2010
Page reviewed: June 29, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.