Volume 13, Number 4—April 2007
Dispatch
Genetic Characterization of HPAI (H5N1) Viruses from Poultry and Wild Vultures, Burkina Faso
Figure 1
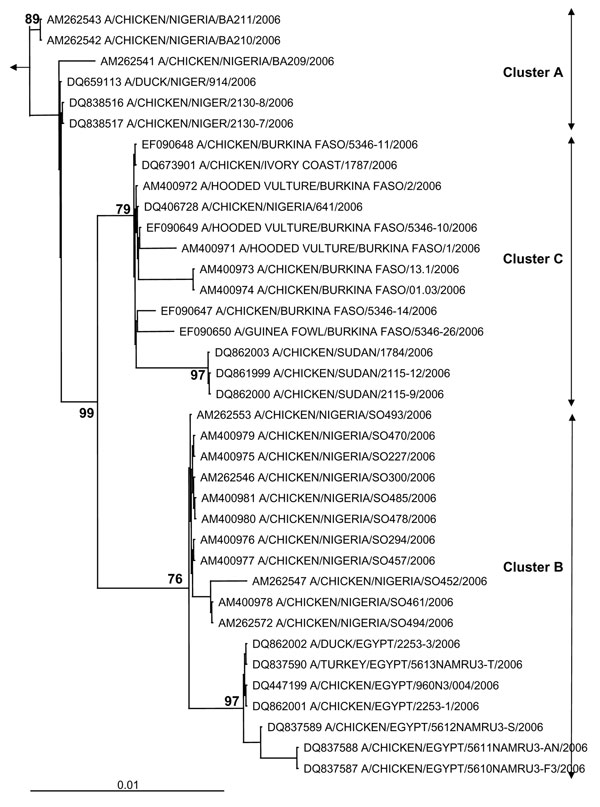
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree for the hemagglutinin (HA) gene of African influenza A (H5N1) strains. The maximum likelihood method was used with 100 bootstraps and 3 jumbles (DNA-ML, Phylip version 3.6) to construct a tree for HA1 nucleotide sequences. Bootstrap values of major nodes are shown. The arrow points to the outgroup strain, A/goose/Guangdong/96. As detailed in the text, cluster C regroups highly pathogenic avian influenza (H5N1) strains from Burkina Faso, northern Nigeria, Sudan, and Côte d'Ivoire; cluster A regroups strains from a southwestern Nigerian farm (coded BA) and Niger; and cluster B regroups strains from a southwestern Nigerian farm (coded SO) and Egypt. The scale bar represents ≈1% of nucleotide changes between close relatives.