Volume 13, Number 8—August 2007
Research
Genetic Diversity of Bartonella henselae in Human Infection Detected with Multispacer Typing
Appendix Figure
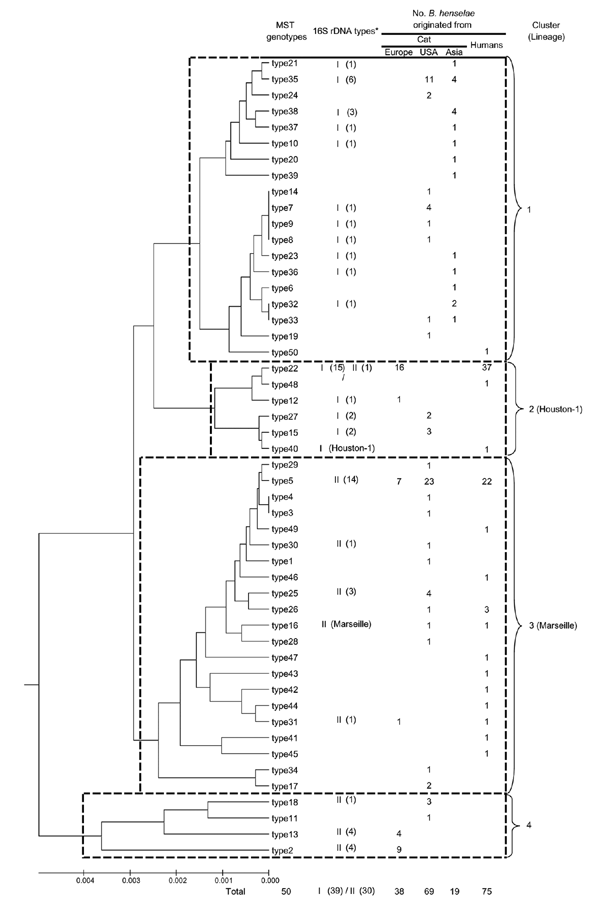
Appendix Figure. Dendrogram showing the phylogenetic organization of the 50 multispacer typing genotypes identified among 126 Bartonella henselae cat isolates and 75 B. henselae isolates detected in humans, constructed by using the neighbor-joining method. Sequences from the 9 spacers were concatenated. The scale bar represents a 1% nucleotide sequence variation. *I = 16S rDNA type I, II = 16S rDNA type II. The number in the brackets indicates the number of B. henselae strains available for determination of 16S rDNA type.
Page created: June 30, 2010
Page updated: June 30, 2010
Page reviewed: June 30, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.