Volume 14, Number 1—January 2008
Research
Cross-subtype Immunity against Avian Influenza in Persons Recently Vaccinated for Influenza
Figure 3
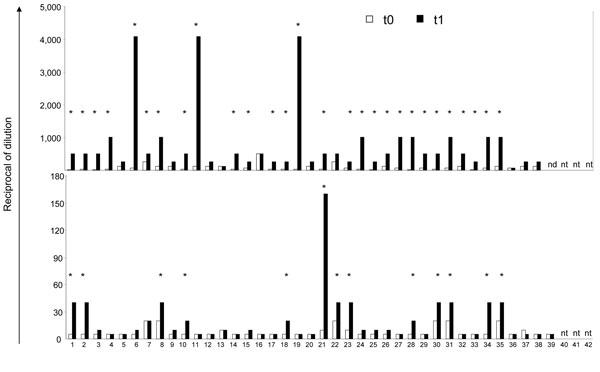
Figure 3. Humoral response against vaccine preparation and influenza virus (H5N1) before (t0) and after (t1) seasonal influenza vaccination. Hemagglutination inhibition (HI) test was used to calculate the antibody (Ab) titer against vaccine preparation (top panel), whereas a neutralization test was used to calculate the antibody titer against influenza (H5N1) (bottom panel) in healthy donors enrolled in the study at baseline (t0) and 1 month after seasonal influenza vaccination (t1). At baseline (white bars), all donors had a detectable level of human influenza antibodies. At t1 (black bars), 28 donors (73.6%) (indicated by *) showed a >4 fold increase of Ab titer against vaccine preparation (HI) over t0. After seasonal influenza vaccination, 13 serum samples (33.3%) (indicated by *) from the study population showed a 20-fold increase of neutralizing Abs against influenza (H5N1) over t0..