Volume 14, Number 10—October 2008
Letter
Human Rhinovirus Group C Infection in Children with Lower Respiratory Tract Infection
Figure
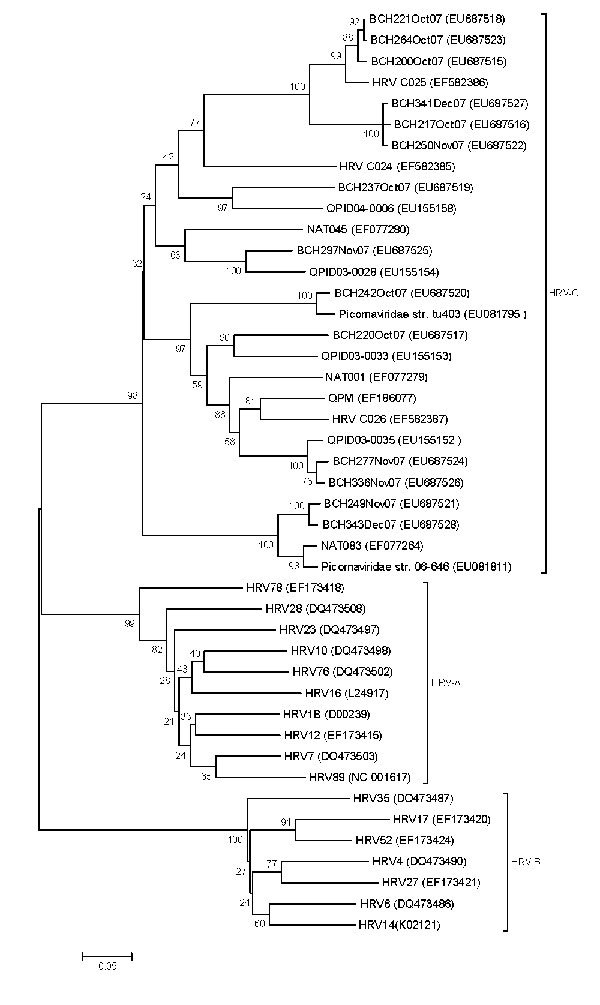
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of the viruses detected in this study based on the nucleotide sequences of the virus capsid protein (VP)4/VP2 region. Using the VP4/VP2 nucleotide sequence (258 nt), we performed neighbor-joining analysis by applying the Kimura 2-parameter model in MEGA software version 4.0 (www.megasoftware.net). Bootstrap values from 1,000 replicates are shown next to the branches. The scale bar indicates evolutionary distance. Representative viruses from the different human respiratory virus (HRV) groups are included. GenBank accession numbers for reference sequences are indicated in parentheses.
Page created: July 13, 2010
Page updated: July 13, 2010
Page reviewed: July 13, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.