Volume 14, Number 2—February 2008
Research
Dissemination of Clonally Related Escherichia coli Strains Expressing Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase CTX-M-15
Appendix Figure
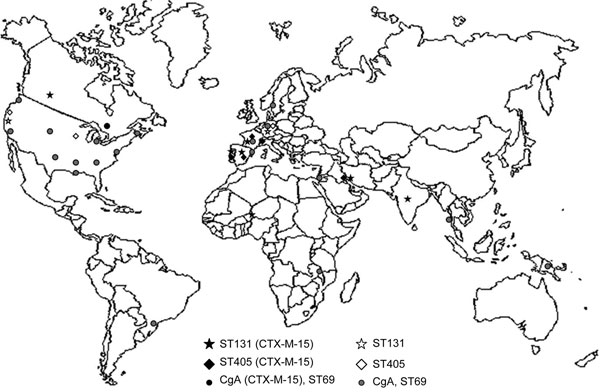
Appendix Figure. Geographic distribution of widely disseminated Escherichia coli clonal complexes associated with CTX-M-15. Data from strains lacking blaCTX-M-15 are from published studies (17,27,28; http://web.mpiib-berlin.mpg.de/mlst/dbs/Ecoli). E. coli clonal group A (CgA) has been identified as different sequence types (STs), most belonging to ST69 (27).
Page created: July 07, 2010
Page updated: July 07, 2010
Page reviewed: July 07, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.