Volume 14, Number 5—May 2008
Dispatch
Naturally Acquired Human Plasmodium knowlesi Infection, Singapore
Figure 2
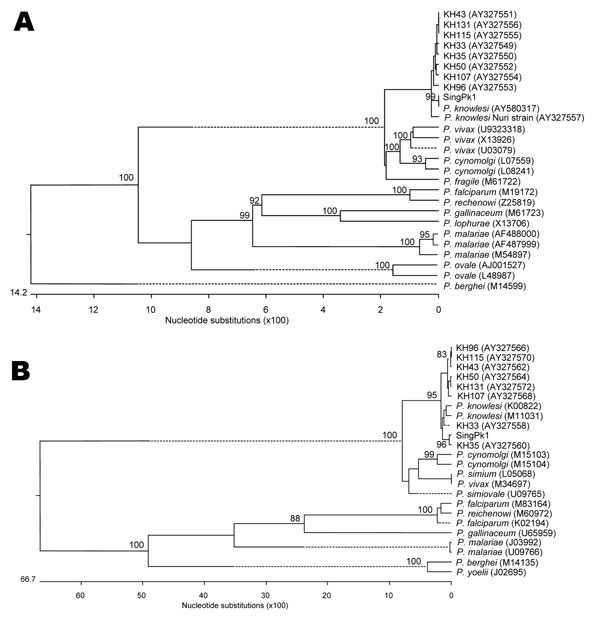
Figure 2. Phylogenetic trees comparing our case sample (denoted as SingPk1) with other Plasmodium species, based on SSU rRNA (A) and csp (B) sequences. Species and sequences used were selected to match those previously reported (5). Figures on the branches are bootstrap percentages based on 1,000 replicates, and only those above 80% are shown. GenBank accession numbers are in parentheses.
References
- Coatney GR, Collins WE, Warren M, Contacos PG. The primate malarias [CD-ROM; original book published 1971]. Version 1.0. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2003.
- Knowles R, Das Gupta BM. A study of monkey-malaria and its experimental transmission to man. Ind Med Gaz. 1932;67:301–20.
- Chin W, Contacos PG, Coatney GR, Kimball HR. A naturally acquired quotidian-type malaria in man transferable to monkeys. Science. 1965;149:865. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fong YL, Cadigan FC, Coatney GR. A presumptive case of naturally occurring Plasmodium knowlesi in man in Malaysia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1971;65:839–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Singh B, Kim Sung L, Matusop A, Radhakrishnan A, Shamsul SS, Cox-Singh J, A large focus of naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi infections in human beings. Lancet. 2004;363:1017–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jongwutiwes S, Putaporntip C, Iwasaki T, Sata T, Kanbara H. Naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in human, Thailand. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:2211–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhu HM, Li J, Zheng H. Human natural infection of Plasmodium knowlesi. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2006;24:70–1.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cox-Singh J, Davis TME, Lee KS, Shamsul SSG, Matusop A, Ratnam S, Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in humans is widely distributed and potentially life threatening. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:165–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chiam PT, Oh HM, Ooi EE. Localised outbreak of Falciparum malaria in Singapore. Singapore Med J. 2003;44:357–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Singh B, Bobogare A, Cox-Singh J, Snounou G, Abdullah MS, Rahman HA. A genus- and species-specific nested polymerase chain reaction malaria detection assay for epidemiologic studies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;60:687–92.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rougemont M, Van Saanen M, Sahli R, Hinrikson HP, Bille J, Haton K. Detection of four Plasmodium species in blood from humans by 18S rRNA gene subunit-based and species specific real-time PCR assays. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:5636–43. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McCutchan TF, Kissinger JC, Touray MG, Rogers MJ, Li J, Sullivan M, Comparison of circumsporozoite proteins from avian and mammalian malarias: biological and phylogenetic implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:11889–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chin W, Contacos PG, Collins WE, Jether MH, Alpert E. Experimental mosquito-transmission of Plasmodium knowlesi to man and monkey. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968;17:355–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yang CMMK. Yong K, Lim KKP. Wild mammals of Singapore. In: Chou LM, PKL Ng. Essays in zoology, papers commemorating the 40th anniversary of the Department of Zoology. Singapore: National University of Singapore; 1990. p. 1–24.
Page created: July 08, 2010
Page updated: July 08, 2010
Page reviewed: July 08, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.