Volume 14, Number 5—May 2008
Research
Cryptococcus neoformans Strains and Infection in Apparently Immunocompetent Patients, China
Figure 3
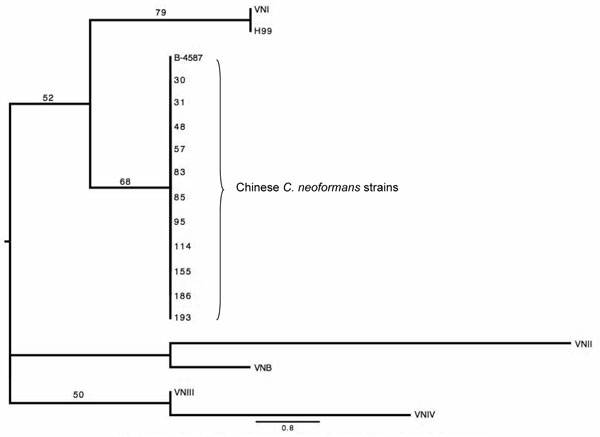
Figure 3. The phylogenetic tree for maximum parsimony analysis composed on the basis of the M13-PCR pattern of 12 Chinese Cryptococcus neoformans strains. Numbers above the branches represent bootstrap support percentages based on 500 replicates. The scale bar represents the inferred number of steps along a branch of the tree.
Page created: July 08, 2010
Page updated: July 08, 2010
Page reviewed: July 08, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.