Volume 14, Number 5—May 2008
Letter
Persistent Human Metapneumovirus Infection in Immunocompromised Child
Figure
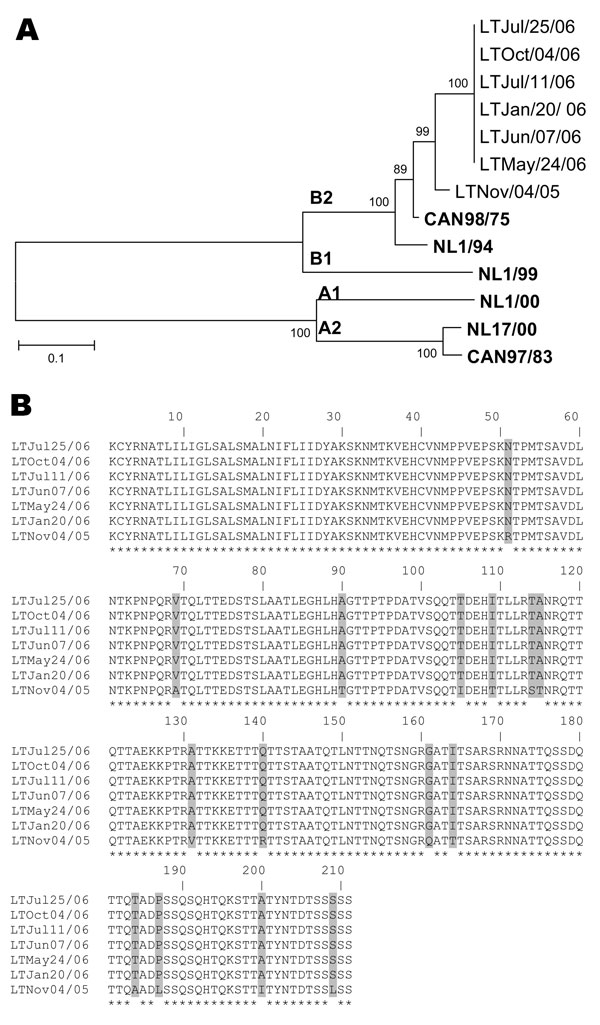
Figure. A) Phylogenetic analysis of human metapneumovirus (hMPV) strains isolated during an 11-month period based on nucleotide sequences of the G gene. Multiple nucleotide sequence alignments were performed by using the ClustalW program (www.molecularevolution.org/cdc/software/clustalw); a phylogenetic tree was constructed with MEGA 3.1 software (www.megasoftware.net) by using the neighbor-joining algorithm with Kimura-2 parameters. The analysis included the following hMPV reference strains: Can98/75 (GenBank accession no. AY485245), NL1/94 (AY304362), NL1/99 (AY304361), NL1/00 (AF371337), NL17/00 (AY304360), and Can97/83 (AY485253). Scale bar indicates 1 substitution for every 10 nucleic acid residues. Boldface indicates reference isolates. B) Comparison of the partial amino acid sequences (residues 26–236) of the G protein of hMPV isolates recovered during an 11-month period from an immunocompromised child. Asterisks denote identical residues; shaded boxes highlight different amino acids between the hMPV variant of November 4, 2005, and the subsequent variants from January 20, 2006, to October 4, 2006.