Volume 15, Number 5—May 2009
Dispatch
Clostridium difficile in Retail Meat Products, USA, 2007
Figure
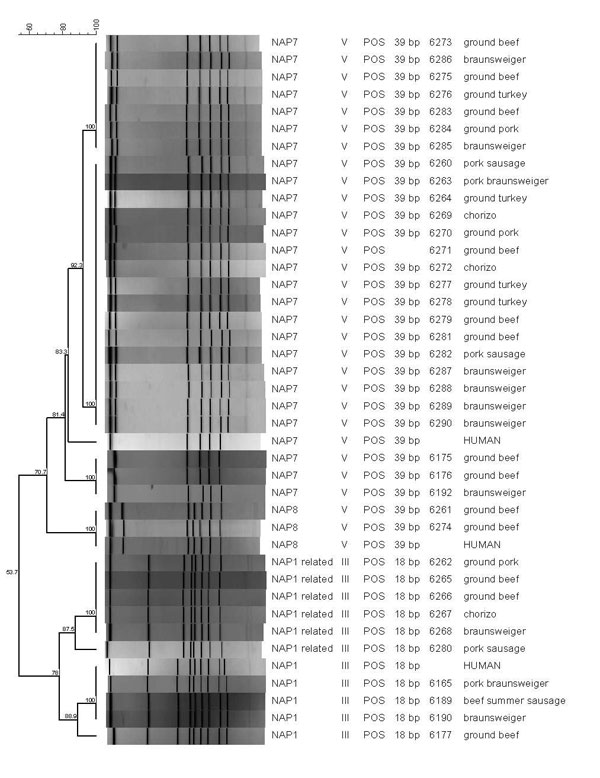
Figure. Origin, NAP types, and relatedness of strains from foods and humans, Arizona, USA, 2007. All strains were positive by PCR for binary toxin. Scale bar indicates genetic relatedness. Tox, toxinotype; Ref, reference; NAP1-r, NAP1-related.
Page created: December 16, 2010
Page updated: December 16, 2010
Page reviewed: December 16, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.