Volume 16, Number 1—January 2010
Research
Norovirus Gastroenteritis Outbreak with a Secretor-independent Susceptibility Pattern, Sweden
Figure 2
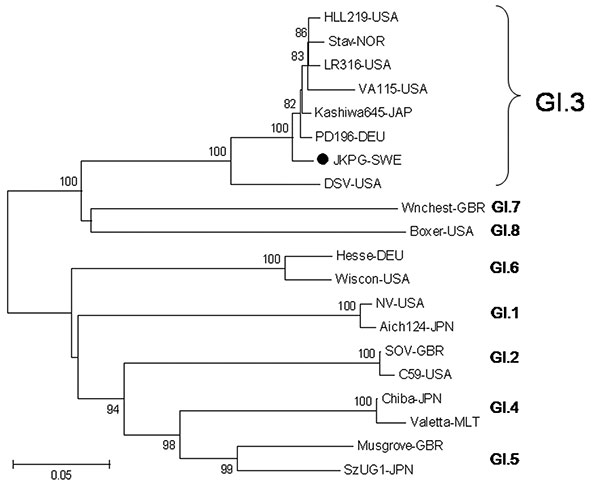
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of amino acids of the norovirus capsid gene from the gastroenteritis outbreak in Jönköping, Sweden (JKPG, •) and reference strains. The tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining and Poisson correction methods, with MEGA 4.0 software (www.megasoftware.net). Bootstrap values are shown at the branch nodes (values <70% are not shown). Reference sequences were collected from Genbank and represent the 8 genotypes of GI as described by Zheng et al. (26). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. NV-USA [M87661], Aich124-JPN [AB031013], SOV-GBR [L07418], C59-USA [AF435807], HLL219-USA [AF414403], Stav-Nor [AF145709], LR316-USA [AF414405], VA115-USA [AY038598], Kashiwa645-JAP [BD011871], PD196-DEU [AF439267], JKPG-SWE [FJ711163] DSV-USA [U04469], Chiba-JPN [AB042808], Valetta-MLT [AJ277616], Musgrove-GBR [AJ277614], SzUG1-JPN [AB039774], Hesse-DEU [AF093797], Wiscon-USA [AY502008], Wnchest-GBR [AJ277609], Boxer-USA [AF538679].
References
- Hedlund KO, Rubilar-Abreu E, Svensson L. Epidemiology of calicivirus infections in Sweden, 1994–1998. J Infect Dis. 2000;181(Suppl 2):S275–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Inouye S, Yamashita K, Yamadera S, Yoshikawa M, Kato N, Okabe N. Surveillance of viral gastroenteritis in Japan: pediatric cases and outbreak incidents. J Infect Dis. 2000;181(Suppl 2):S270–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lopman BA, Reacher MH, Van Duijnhoven Y, Hanon FX, Brown D, Koopmans M. Viral gastroenteritis outbreaks in Europe, 1995–2000. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:90–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fankhauser RL, Monroe SS, Noel JS, Humphrey CD, Bresee JS, Parashar UD, Epidemiologic and molecular trends of “Norwalk-like viruses” associated with outbreaks of gastroenteritis in the United States. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:1–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Widdowson MA, Sulka A, Bulens SN, Beard RS, Chaves SS, Hammond R, Norovirus and foodborne disease, United States, 1991–2000. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:95–102.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bucardo F, Kindberg E, Paniagua M, Vildevall M, Svensson L. Genetic susceptibility to symptomatic norovirus infection in Nicaragua. J Med Virol. 2009;81:728–35. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kindberg E, Akerlind B, Johnsen C, Knudsen JD, Heltberg O, Larson G, Host genetic resistance to symptomatic norovirus (GGII.4) infections in Denmark. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:2720–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lindesmith L, Moe C, Marionneau S, Ruvoen N, Jiang X, Lindblad L, Human susceptibility and resistance to Norwalk virus infection. Nat Med. 2003;9:548–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thorven M, Grahn A, Hedlund KO, Johansson H, Wahlfrid C, Larson G, A homozygous nonsense mutation (428G→A) in the human secretor (FUT2) gene provides resistance to symptomatic norovirus (GGII) infections. J Virol. 2005;79:15351–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tan M, Jin M, Xie H, Duan Z, Jiang X, Fang Z. Outbreak studies of a GII-3 and a GII-4 norovirus revealed an association between HBGA phenotypes and viral infection. J Med Virol. 2008;80:1296–301. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hutson AM, Airaud F, Le Pendu J, Estes MK, Atmar RL. Norwalk virus infection associates with secretor status genotyped from sera. J Med Virol. 2005;77:116–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Koda Y, Soejima M, Kimura H. The polymorphisms of fucosyltransferases. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2001;3:2–14.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kelly RJ, Rouquier S, Giorgi D, Lennon GG, Lowe JB. Sequence and expression of a candidate for the human secretor blood group alpha(1,2)fucosyltransferase gene (FUT2). Homozygosity for an enzyme-inactivating nonsense mutation commonly correlates with the non-secretor phenotype. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:4640–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shirato H, Ogawa S, Ito H, Sato T, Kameyama A, Narimatsu H, Noroviruses distinguish between type 1 and type 2 histo-blood group antigens for binding. J Virol. 2008;82:10756–67. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huang P, Farkas T, Zhong W, Tan M, Thornton S, Morrow AL, Norovirus and histo-blood group antigens: demonstration of a wide spectrum of strain specificities and classification of two major binding groups among multiple binding patterns. J Virol. 2005;79:6714–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huang P, Farkas T, Marionneau S, Zhong W, Ruvoen-Clouet N, Morrow AL, Noroviruses bind to human ABO, Lewis, and secretor histo-blood group antigens: identification of 4 distinct strain-specific patterns. J Infect Dis. 2003;188:19–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lindesmith LC, Donaldson EF, Lobue AD, Cannon JL, Zheng DP, Vinje J, Mechanisms of GII.4 norovirus persistence in human populations. PLoS Med. 2008;5:e31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Le Pendu J, Ruvoen-Clouet N, Kindberg E, Svensson L. Mendelian resistance to human norovirus infections. Semin Immunol. 2006;18:375–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lindesmith L, Moe C, Lependu J, Frelinger JA, Treanor J, Baric RS. Cellular and humoral immunity following Snow Mountain virus challenge. J Virol. 2005;79:2900–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rockx BH, Vennema H, Hoebe CJ, Duizer E, Koopmans MP. Association of histo-blood group antigens and susceptibility to norovirus infections. J Infect Dis. 2005;191:749–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kindberg E, Hejdeman B, Bratt G, Wahren B, Lindblom B, Hinkula J, A nonsense mutation (428G→A) in the fucosyltransferase FUT2 gene affects the progression of HIV-1 infection. AIDS. 2006;20:685–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rydell GE, Nilsson J, Rodriguez-Diaz J, Ruvoen-Clouet N, Svensson L, Le Pendu J, Human noroviruses recognize sialyl Lewis x neoglycoprotein. Glycobiology. 2009;19:309–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bucardo F, Nordgren J, Carlsson B, Paniagua M, Lindgren PE, Espinoza F, Pediatric norovirus diarrhea in Nicaragua. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:2573–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nordgren J, Bucardo F, Dienus O, Svensson L, Lindgren PE. Novel light-upon-extension real-time PCR assays for detection and quantification of genogroup I and II noroviruses in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:164–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kojima S, Kageyama T, Fukushi S, Hoshino FB, Shinohara M, Uchida K, Genogroup-specific PCR primers for detection of Norwalk-like viruses. J Virol Methods. 2002;100:107–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zheng DP, Ando T, Fankhauser RL, Beard RS, Glass RI, Monroe SS. Norovirus classification and proposed strain nomenclature. Virology. 2006;346:312–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Larsson MM, Rydell GE, Grahn A, Rodriguez-Diaz J, Akerlind B, Hutson AM, Antibody prevalence and titer to norovirus (genogroup II) correlate with secretor (FUT2) but not with ABO phenotype or Lewis (FUT3) genotype. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:1422–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hutson AM, Atmar RL, Graham DY, Estes MK. Norwalk virus infection and disease is associated with ABO histo-blood group type. J Infect Dis. 2002;185:1335–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Halperin T, Vennema H, Koopmans M, Kahila Bar-Gal G, Kayouf R, Sela T, No association between histo-blood group antigens and susceptibility to clinical infections with genogroup II norovirus. J Infect Dis. 2008;197:63–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar