Volume 16, Number 1—January 2010
Dispatch
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Multilocus Sequence Types in Guatemala and Mexico
Figure
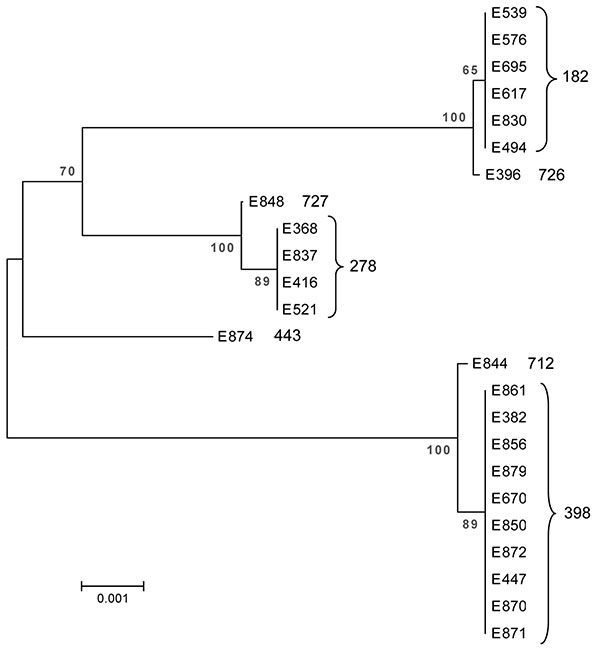
Figure. Dendrogram of the 24 enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains from Guatemala and Mexico included in the study, showing multilocus sequence type. Sequences were assembled with BioEdit and aligned using ClustalX within BioEdit (12). The dendogram represents the relationship of a concatenation of the sequences from each strain and was constructed by using MEGA 3.1 (13). Phylogenetic reconstructions were created by using the neighbor-joining method with the Kimura 2-parameter substitution model, using 1,000 bootstrap replicates. A similar arrangement of the strains was indicated by eBURST version 2 analysis (http://eburst.mlst.net). Scale bar indicates dissimilarity, where 0 is completely identical and 1 is completely dissimilar.
References
- Qadri F, Svennerholm A-M, Faruque AS, Sack RB. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in developing countries: epidemiology, microbiology, clinical features, treatment, and prevention. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18:465–83. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wolf MK. Occurence, distribution, and associations of O and H serogroups, colonization factor antigens, and toxins of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1997;10:569–84.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bölin I, Wiklund G, Qadri F, Torres O, Bourgeois AL, Savarino S, Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli with STh and STp genotypes is associated with diarrhea both in children in areas of endemicity and in travelers. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:3872–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gaastra W, Svennerholm A-M. Colonization factors of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Trends Microbiol. 1996;4:444–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sack DA, Shimko J, Torres O, Bourgeois AL, Francia DS, Gustafsson B, Randomised, double-blind, safety and efficacy of a killed oral vaccine for enterotoxigenic E. coli diarrhoea of travellers to Guatemala and Mexico. Vaccine. 2007;25:4392–400. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shaheen HI, Abdel Messih IA, Klena JD, Mansour A, El-Wakkeel Z, Wierzba TF, Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in samples obtained from Egyptian children presenting to referral hospitals. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:189–97. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Qadri F, Saha A, Ahmed T, Al Tarique A, Ara Begum Y, Svennerholm A-M. Disease burden due to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in the first 2 years of life in an urban community in Bangladesh. Infect Immun. 2007;75:3961–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bourgeois AL, Halpern J, Gustafsson B, Svennerholm A-M, Torres O, Belkind-Gerson J, Protective efficacy of an oral killed vaccine (OKV) for enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) in adult travelers to Guatemala (GU) and Mexico (MX). 45th Annual Meeting of the Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2005.
- Taylor DN, Bourgeois AL, Ericsson CD, Steffen R, Jiang ZD, Halpern J, A randomized, double-blind, multicenter study of rifaximin compared with placebo and with ciprofloxacin in the treatment of travelers’ diarrhea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006;74:1060–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sjöling Å, Wiklund G, Savarino SJ, Cohen DI, Svennerholm A-M. Comparative analyses of phenotypic and genotypic methods for detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) toxins and colonisation factors. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:3295–301. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wirth T, Falush D, Lan R, Colles F, Mensa P, Wieler LH, Sex and virulence in Escherichia coli: an evolutionary perspective. Mol Microbiol. 2006;60:1136–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1999;41:95–8.
- Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA3: Integrated software for Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform. 2004;5:150–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nicklasson M, Sjöling Å, Lebens M, Tobias J, Janzon A, Brive L, Mutations in the periplasmic chaperone leading to loss of surface expression of the colonization factor CS6 in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) clinical isolates. Microb Pathog. 2008;44:246–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wolf MK, de Haan LA, Cassels FJ, Willshaw GA, Warren R, Boedeker EC, The CS6 colonization factor of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli contains two heterologous major subunits. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1997;148:35–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: March 31, 2011
Page updated: March 31, 2011
Page reviewed: March 31, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.