Volume 16, Number 12—December 2010
Research
Bartonella spp. in Bats, Kenya
Figure 1
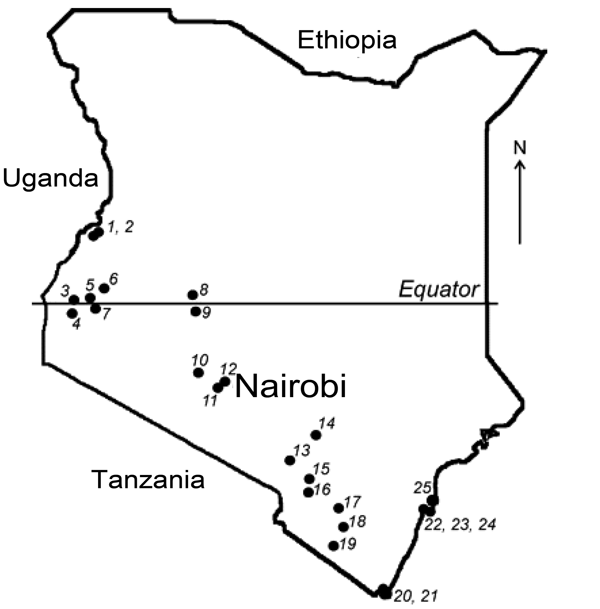
Figure 1. Field sites where bats were collected in Kenya. Numbers identify collection sites (5).
References
- Halpin K, Young PL, Field HE, Mackenzie JS. Isolation of Hendra virus from pteropid bats: a natural reservoir of Hendra virus. J Gen Virol. 2000;81:1927–32.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li W, Shi Z, Yu M, Ren W, Smith C, Epstein JH, Bats are natural reservoirs of SARS-like coronaviruses. Science. 2005;310:676–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang LF, Shi Z, Zhang S, Field H, Daszak P, Eaton BT. Review of bats and SARS. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1834–40.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Williams CJ. Bats as the reservoir for outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases. Euro Surveill. 2005;10(11):E051110.4. PMID: 16794279
- Kuzmin IV, Niezgoda M, Franka R, Agwanda B, Markotter W, Beagley JC, Lagos bat virus in Kenya. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:1451–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T. Bats: important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:531–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bennett M. Bats and human emerging diseases. Epidemiol Infect. 2006;134:905–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van der Poel WH, Lina PH, Kramps JA. Public health awareness of emerging zoonotic viruses of bats: a European perspective. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2006;6:315–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ghatak S, Banerjee R, Agarwal RK, Kapoor KN. Zoonoses and bats: a look from human health viewpoint. J Commun Dis. 2000;32:40–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Evans NJ, Bown K, Timofte D, Simpson VR, Birtles RJ. Fatal borreliosis in bat caused by relapsing fever spirochete, United Kingdom. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1331–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Concannon R, Wynn-Owen K, Simpson VR, Birtles RJ. Molecular characterization of haemoparasites infecting bats (Microchiroptera) in Cornwall, UK. Parasitology. 2005;131:489–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Loftis AD, Gill JS, Schriefer ME, Levin ML, Eremeeva ME, Gilchrist MJ, Detection of Rickettsia, Borrelia, and Bartonella in Carios kelleyi (Acari: Argasidae). J Med Entomol. 2005;42:473–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reeves WK, Loftis AD, Gore JA, Dasch GA. Molecular evidence for novel Bartonella species in Trichobius major (Diptera: Streblidae) and Cimex adjunctus (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) from two southeastern bat caves. U.S.A. J Vector Ecol. 2005;30:339–41.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reeves WK, Rogers TE, Durden LA, Dasch GA. Association of Bartonella with the fleas (Siphonaptera) of rodents and bats using molecular techniques. J Vector Ecol. 2007;32:118–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Birtles RJ. Bartonellae as elegant hemotropic parasites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1063:270–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dehio C. Bartonella interactions with endothelial cells and erythrocytes. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9:279–85. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chomel BB, Boulouis HJ, Breitschwerdt EB, Kasten RW, Vayssier-Taussat M, Birtles RJ, Ecological fitness and strategies of adaptation of Bartonella species to their hosts and vectors. Vet Res. 2009;40:29. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kosoy M, Regnery R, Tzianabos T, Marston E, Jones D, Green D, Distribution, diversity and host specificity of Bartonella in rodents from the southeastern United States. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;57:578–88.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Anderson B, Neuman MA. Bartonella spp. as emerging human pathogens. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1997;10:203–19.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Daly JS, Worthington MG, Brenner DJ, Moss CW, Hollis DG, Weyant RS, Rochalimaea elizabethae sp. nov. isolated from a patient with endocarditis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993;31:872–81.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Welch DF, Carroll KC, Hofmeister EK, Persing DH, Robison DA, Steigerwalt AG, Isolation of a new subspecies, Bartonella vinsonii subsp. arupensis, from a cattle rancher: identity with isolates found in conjunction with Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti among naturally infected mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:2598–601.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kerkhoff FT, Bergmans AM, van Der Zee A, Rothova A. Demonstration of Bartonella grahamii DNA in ocular fluids of a patient with neuroretinitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:4034–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kosoy M, Murray M, Gilmore RD, Bai Y, Gage KL. Bartonella strains from ground squirrels are identical to Bartonella washoensis isolated from a human patient. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:645–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Breitschwerdt EB, Kordick DL. Bartonella infection in animals: carriership, reservoir potential, pathogenicity, and zoonotic potential for human infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000;13:428–38. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Roux V, Eykyn SJ, Wyllie S, Raoult D. Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii as an agent of afebrile blood culture–negative endocarditis in a human. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:1698–700.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Eremeeva ME, Gerns HL, Lydy SL, Goo JS, Ryan ET, Mathew SS, Bacteremia, fever, and splenomegaly caused by a newly recognized Bartonella species. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2381–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kosoy M, Morway C, Sheff K, Bai Y, Colborn J, Chalcraft L, Bartonella tamiae sp. nov., a newly recognized pathogen isolated from three human patients from Thailand. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:772–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- La Scola B, Zeaiter Z, Khamis A, Raoult D. Gene-sequence-based criteria for species definition in bacteriology: the Bartonella paradigm. Trends Microbiol. 2003;11:318–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kosoy M, Mandel E, Green D, Marston E, Jones D, Childs J. Prospective studies of Bartonella of rodents. Part II. Diverse infections in a single rodent community. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2004;4:296–305. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Billeter SA, Levy MG, Chomel BB, Breitschwerdt EB. Vector transmission of Bartonella species with emphasis on the potential for tick transmission. Med Vet Entomol. 2008;22:1–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dick CW, Patterson BD. Bat flies: obligate ectoparasites of bats. Micromammals and macroparasites: from evolutionary ecology to management. Morand S, et al. (Eds). Springer-Verlag, Tokyo, Japan, 2006;179–94.
- Kuzmin IV, Mayer AE, Niezgoda M, Markotter W, Agwanda B, Breiman RF, Shimoni bat virus, a new representative of the Lyssavirus genus. Virus Res. 2010;149:197–210. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tong S, Conrardy C, Ruone S, Kuzmin IV, Guo X, Tao Y, Detection of novel SARS-like and other coronaviruses in bats from Kenya. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:482–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Drexler JF, Corman VM, Gloza-Rausch F, Seebens A, Annan A, Ipsen A, Henipavirus RNA in African bats. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e6367. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Towner JS, Amman BR, Sealy TK, Carroll SA, Comer JA, Kemp A, Isolation of genetically diverse Marburg viruses from Egyptian fruit bats. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000536. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: August 28, 2011
Page updated: August 28, 2011
Page reviewed: August 28, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.