Volume 16, Number 3—March 2010
Dispatch
Banna Virus, China, 1987–2007
Figure 2
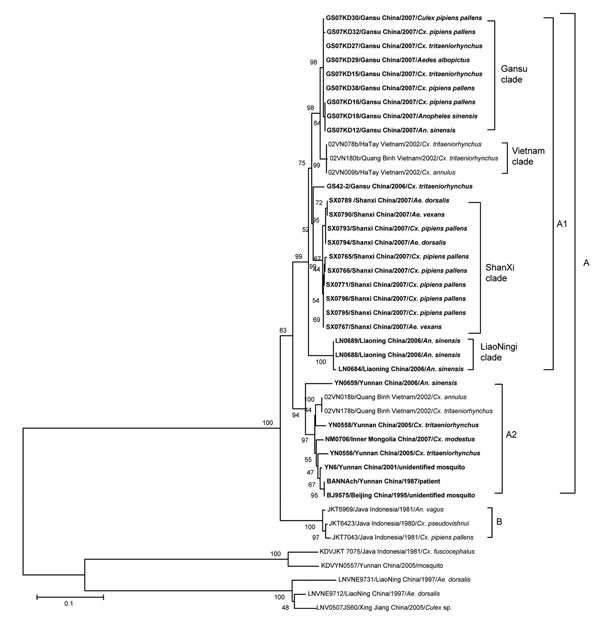
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis based on the complete coding sequence of the 12th segment of Banna viruses (BAVs) currently isolated. Phylogenetic analyses were performed by the neighbor-joining method using MEGA version 4 software (www.megasoftware.net). Bootstrap probabilities of each node were calculated with 1,000 replicates. The tree was rooted by using Kadipiro virus and Liaoning virus as the outgroup viruses. Scale bars indicate a genetic distance of 0.1-nt substitutions per site. Isolates obtained in China are in boldface. Viruses were identified by using the nomenclature of virus strain/country/year of isolation/origin.
Page created: December 14, 2010
Page updated: December 14, 2010
Page reviewed: December 14, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.