Volume 16, Number 4—April 2010
Letter
Patients with Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 in Intensive Care Units, Israel
Figure
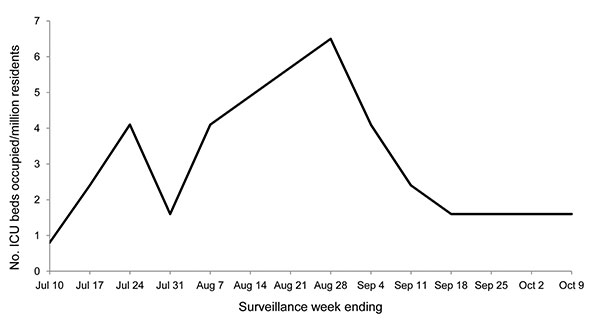
Figure. Number of intensive care unit (ICU) beds occupied by patients with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 infection in district ICUs during the described surveillance period, Tel Aviv, Israel. During this period, 5.7% of ICU beds, on average, were continuously occupied by patients with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 infection. The occupancy peak was 6.5 of 53.8 standardized ICU beds per million residents (12.1%) during the week ending August 28, 2009. Data are per million residents.
Page created: December 28, 2010
Page updated: December 28, 2010
Page reviewed: December 28, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.