Volume 16, Number 9—September 2010
Dispatch
Co-infections with Plasmodium knowlesi and Other Malaria Parasites, Myanmar
Figure
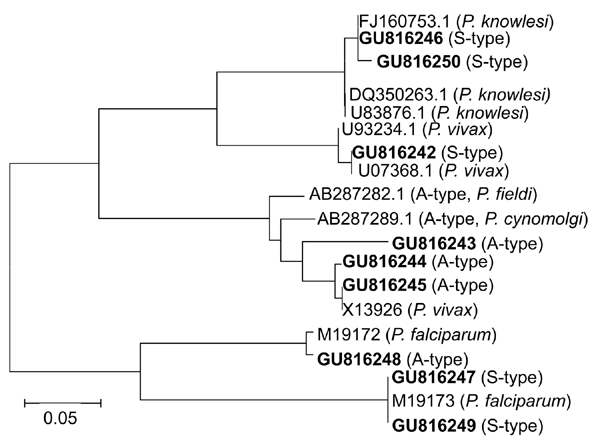
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of A-type and S-type 18S small subunit (SSU) rRNA gene sequences of Plasmodium spp., Myanmar, 2008. Fragments of 18S SSU rRNA gene sequences of samples were analyzed by aligning with published homologous sequences of P. falciparum, P. vivax, and P. knowlesi. A phylogenetic tree was constructed on the basis of similarities by using MEGA version 4.1 (13). Novel sequences identified in this study are indicated in boldface. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- McKenzie FE, Bossert WH. Mixed-species Plasmodium infections of humans. J Parasitol. 1997;83:593–600. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Singh B, Kim Sung L, Matusop A, Radhakrishnan A, Shamsul SS, Cox-Singh J, A large focus of naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi infections in human beings. Lancet. 2004;363:1017–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Putaporntip C, Hongsrimuang T, Seethamchai S, Kobasa T, Limkittikul K, Cui L, Differential prevalence of Plasmodium infections and cryptic Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in humans in Thailand. J Infect Dis. 2009;199:1143–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Butcher GA, Mitchell GH, Cohen S. Plasmodium knowlesi infections in a small number of non-immune natural hosts (Macaca fascicularis) and in rhesus monkeys (M. mulatta). Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2010;104:75–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cox-Singh J, Singh B. Knowlesi malaria: newly emergent and of public health importance? Trends Parasitol. 2008;24:406–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cox-Singh J, Davis TM, Lee KS, Shamsul SS, Matusop A, Ratnam S, Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in humans is widely distributed and potentially life threatening. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:165–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bronner U, Divis PC, Färnert A, Singh B. Swedish traveler with Plasmodium knowlesi malaria after visiting Malaysian Borneo. Malar J. 2009;8:15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Hellemond JJ, Rutten M, Koelewijn R, Zeeman AM, Verweij JJ, Wismans PJ, Human Plasmodium knowlesi infection detected by rapid diagnostic tests for malaria. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1478–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee KS, Cox-Singh J, Brooke G, Matusop A, Singh B. Plasmodium knowlesi from archival blood films: further evidence that human infections are widely distributed and not newly emergent in Malaysian Borneo. Int J Parasitol. 2009;39:1125–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhu HM, Li J, Zheng H. Human natural infection of Plasmodium knowlesi [in Chinese]. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2006;24:70–1. PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bereczky S, Mårtensson A, Gil JP, Färnert A. Short report: Rapid DNA extraction from archive blood spots on filter paper for genotyping of Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;72:249–51. PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Singh B, Bobogare A, Cox-Singh J, Snounou G, Abdullah MS, Rahman HA. A genus- and species-specific nested polymerase chain reaction malaria detection assay for epidemiologic studies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;60:687–92. PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ng OT, Ooi EE, Lee CC, Lee PJ, Ng LC, Pei SW, Naturally acquired human Plasmodium knowlesi infection, Singapore. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:814–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Imwong M, Tanomsing N, Pukrittayakamee S, Day NP, White NJ, Snounou G. Spurious amplification of a Plasmodium vivax small-subunit RNA gene by use of primers currently used to detect P. knowlesi. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:4173–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kawai S, Hirai M, Haruki K, Tanabe K, Chigusa Y. Cross-reactivity in rapid diagnostic tests between human malaria and zoonotic simian malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi infections. Parasitol Int. 2009;58:300–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: August 28, 2011
Page updated: August 28, 2011
Page reviewed: August 28, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.