Volume 17, Number 10—October 2011
Research
Humans Infected with Relapsing Fever Spirochete Borrelia miyamotoi, Russia
Figure 3
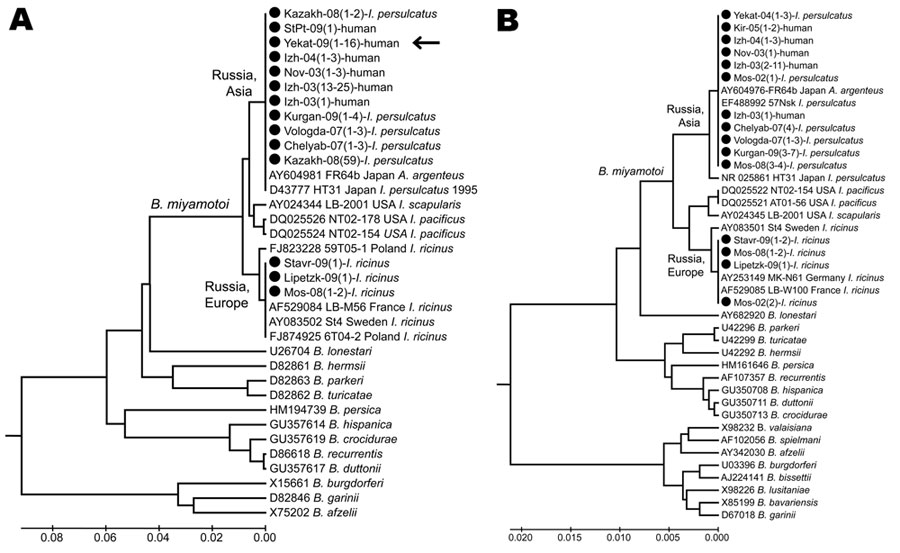
Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree of Borrelia spp. detected in persons and ticks, based on flagellin gene fragment (A) and16S rRNA gene fragment (B). Sequences were aligned and analyzed by using MEGA4.1 software (www.megasoftware.net). Genetic trees were constructed from the partial nucleotide sequences of the flagellin gene and the 16S rRNA gene by using the Kimura 2-parameter model and the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean. Arrow indicates the 16 Borrelia spp. from Yekaterinburg in 2009 that had the same nucleotide sequence. Circles indicate sequences that we listed in GenBank (accession nos. GU797331–GU797346 and JF951378–JF951392). Sequences for B. burgdorferi sensu lato and relapsing fever borreliae are shown for comparison. Scale bars indicate genetic distance.