Volume 17, Number 10—October 2011
Dispatch
Global Distribution of Shigella sonnei Clones
Figure
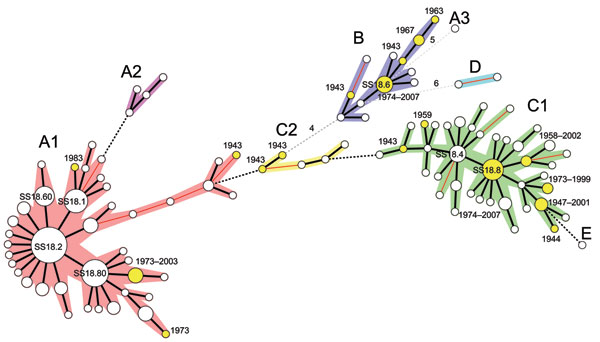
Figure. Clonal structure of 200 Shigella sonnei isolates. These isolates, representative of the 1,672 isolates analyzed in this study, were selected by obtaining 1 isolate for 1 multilocus variable number tandem repeat analysis (MLVA) 18 type from those identified in each of 50 countries on 5 continents (Africa, Asia, Europe, North America, and South America) and the Pacific region. The tree was constructed by using MLVA18 profiles and a minimum spanning tree algorithm. Circle size is proportional to the number of countries detected with the MLVA18 type. Genotypes in yellow indicate isolates obtained in the early period (1943–1983). A cluster or subcluster containing >2 genotypes differing at <2 loci is indicated by the 5 other colors. Distances of 1 locus between 2 closest genotypes are indicated by thick black lines, distances of 2 loci are indicated by thin red lines, distances of 3 loci are indicated by black dashed lines, and distances >4 loci are indicated by grey dashed lines. Numbers of different loci are indicated.