Volume 17, Number 10—October 2011
Research
Plasmodium knowlesi Malaria in Humans and Macaques, Thailand
Figure 2
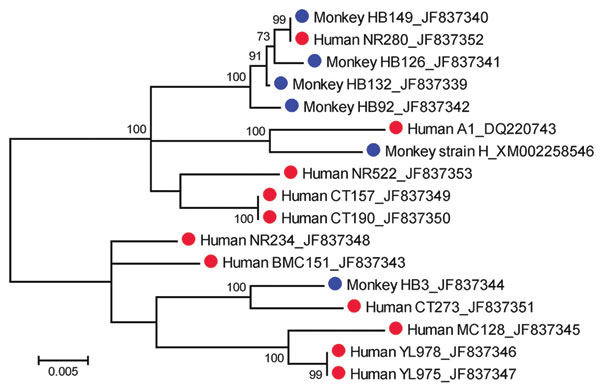
Figure 2. Maximum-likelihood tree inferred from the complete merozoite surface protein 1 gene sequences of Plasmodium knowlesi from humans (red circles) and macaques (blue circles). The tree is drawn to scale, and branch lengths are measured in number of substitutions per site by using MEGA version 5.01 (14). Bootstrap values >50% from 1,000 iterations are shown. Human isolates are from the following provinces: Narathiwat (NR280, NR234, and NR522); Yala (YL975 and YL978); Chantaburi (CT157, CT190, and CT273); and Prachuab Khirikhan (BMC151, MC128, and DQ220743). Isolates HB3, HB92, HB126, HB132, and HB149 are from macaques in Narathiwat Province. GenBank accession nos. are shown after isolate names.
References
- Coatney GR, Collins WE, Warren M, Contacos PG. The primate malarias [CD-ROM]. Version 1.0 (originally published in 1971). Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2003.
- Chin W, Contacos PG, Coatney GR, Kimball HR. A naturally acquired quotidian-type malaria in man transferable to monkeys. Science. 1965;149:865. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jongwutiwes S, Putaporntip C, Iwasaki T, Sata T, Kanbara H. Naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in human, Thailand. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:2211–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Singh B, Kim Sung L, Matusop A, Radhakrishnan A, Shamsul SS, Cox-Singh J, A large focus of naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi infections in human beings. Lancet. 2004;363:1017–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Putaporntip C, Buppan P, Jongwutiwes S. Improved performance with saliva and urine as alternative DNA sources for malaria diagnosis by mitochondrial DNA-based PCR assays. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011; [Epub ahead of print].
- Cox-Singh J, Davis TM, Lee KS, Shamsul SS, Matusop A, Ratnam S, Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in humans is widely distributed and potentially life threatening. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:165–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Putaporntip C, Hongsrimuang T, Seethamchai S, Kobasa T, Limkittikul K, Cui L, Differential prevalence of Plasmodium infections and cryptic Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in humans in Thailand. J Infect Dis. 2009;199:1143–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Daneshvar C, Davis TM, Cox-Singh J, Rafa’ee MZ, Zakaria SK, Divis PC, Clinical and laboratory features of human Plasmodium knowlesi infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:852–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thimasarn K, Jatapadma S, Vijaykadga S, Sirichaisinthop J, Wongsrichanalai C. Epidemiology of malaria in Thailand. J Travel Med. 1995;2:59–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Annual statistics, Division of Vector-Borne Diseases, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand [cited 2011 Feb 14]. www.thaivbd.org/cms/index.php?option=com_frontpage&Itemid=1
- Putaporntip C, Jongwutiwes S, Thongaree S, Seethamchai S, Grynberg P, Hughes AL. Ecology of malaria parasites infecting Southeast Asian macaques: evidence from cytochrome b sequences. Mol Ecol. 2010;19:3466–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Putaporntip C, Jongwutiwes S, Iwasaki T, Kanbara H, Hughes AL. Ancient common ancestry of the merozoite surface protein 1 of Plasmodium vivax as inferred from its homologue in Plasmodium knowlesi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2006;146:105–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG. The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:4876–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011. [Epub ahead of print].
- Putaporntip C, Jongwutiwes S, Sakihama N, Ferreira MU, Kho WG, Kaneko A, Mosaic organization and heterogeneity in frequency of allelic recombination of the Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein-1 locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:16348–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhou G, Sirichaisinthop J, Sattabongkot J, Jones J, Bjørnstad ON, Yan G, Spatio-temporal distribution of Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax malaria in Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;72:256–62.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Childs DZ, Cattadori IM, Suwonkerd W, Prajakwong S, Boots M. Spatiotemporal patterns of malaria incidence in northern Thailand. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2006;100:623–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sattabongkot J, Tsuboi T, Zollner GE, Sirichaisinthop J, Cui L. Plasmodium vivax transmission: chances for control? Trends Parasitol. 2004;20:192–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Somboon P, Lines J, Aramrattana A, Chitprarop U, Prajakwong S, Khamboonruang C. Entomological evaluation of community-wide use of lambdacyhalothrin-impregnated bed nets against malaria in a border area of north-west Thailand. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1995;89:248–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Apiwathnasor C, Prommongkol S, Samung Y, Limrat D, Rojruthai B. Potential for Anopheles campestris (Diptera: Culicidae) to transmit malaria parasites in Pa Rai subdistrict (Aranyaprathet, Sa Kaeo Province), Thailand. J Med Entomol. 2002;39:583–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mayxay M, Pukrittayakamee S, Newton PN, White NJ. Mixed-species malaria infections in humans. Trends Parasitol. 2004;20:233–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McKenzie FE, Bossert WH. Mixed-species Plasmodium infections of humans. J Parasitol. 1997;83:593–600. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Price RN, Simpson JA, Nosten F, Luxemburger C, Hkirjaroen L, ter Kuile F, Factors contributing to anemia in uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;65:614–22.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mason DP, McKenzie FE. Blood-stage dynamics and clinical implications of mixed Plasmodium vivax–Plasmodium falciparum infections. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;61:367–74.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gopinathan VP, Subramanian AR. Pernicious syndromes in Plasmodium infections. Med J Aust. 1982;2:568–72.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mayxay M, Pukritrayakamee S, Chotivanich K, Imwong M, Looareesuwan S, White NJ. Identification of cryptic coinfection with Plasmodium falciparum in patients presenting with vivax malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;65:588–92.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- May J, Falusi AG, Mockenhaupt FP, Ademowo OG, Olumese PE, Bienzle U, Impact of subpatent multi-species and multi-clonal plasmodial infections on anaemia in children from Nigeria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2000;94:399–403. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vythilingam I, Noorazian YM, Huat TC, Jiram AI, Yusri YM, Azahari AH, Plasmodium knowlesi in humans, macaques and mosquitoes in peninsular Malaysia. Parasit Vectors. 2008;1:26. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vythilingam I, Tan CH, Asmad M, Chan ST, Lee KS, Singh B. Natural transmission of Plasmodium knowlesi to humans by Anopheles latens in Sarawak, Malaysia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2006;100:1087–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chareonviriyaphap T, Bangs MJ, Ratanatham S. Status of malaria in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2000;31:225–37.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nakazawa S, Marchand RP, Quang NT, Culleton R, Manh ND, Maeno Y. Anopheles dirus co-infection with human and monkey malaria parasites in Vietnam. Int J Parasitol. 2009;39:1533–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sungvornyothin S, Kongmee M, Muenvorn V, Polsomboon S, Bangs MJ, Prabaripai A, Seasonal abundance and blood-feeding activity of Anopheles dirus sensu lato in western Thailand. J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 2009;25:425–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee KS, Cox-Singh J, Brooke G, Matusop A, Singh B. Plasmodium knowlesi from archival blood films: Further evidence that human infections are widely distributed and not newly emergent in Malaysian Borneo. Int J Parasitol. 2009;39:1125–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Van den Eede P, Van HN, Van Overmeir C, Vythilingam I, Duc TN, Hung le X, et al. Human Plasmodium knowlesi infections in young children in central Vietnam. Malar J. 2009;8:249. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McKenzie FE, Smith DL, O’Meara WP, Forney JR, Magill AJ, Permpanich B, Fever in patients with mixed-species malaria. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:1713–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: September 20, 2011
Page updated: September 20, 2011
Page reviewed: September 20, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.