Volume 17, Number 2—February 2011
Research
Next-Generation Sequencing of Coccidioides immitis Isolated during Cluster Investigation
Figure 3
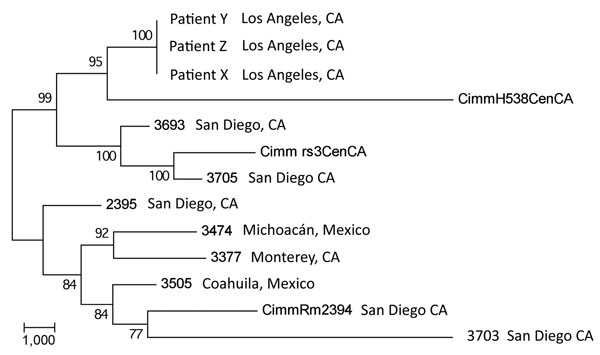
Figure 3. Maximum-parsimony phylogenetic analysis of 13 Coccidioides immitis genomes. MEGA4 (13) was used to conduct maximum-parsimony analysis of all single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) loci common to the 3 transplant isolate genomes and the 10 publicly available C. immitis genome sequences (6,10). A total of 32,695 SNP positions were identified in the final dataset, of which 17,080 were parsimony informative. The percentages of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale; branch lengths were calculated by using the average pathway method (14) and are in the units of the number of changes over the whole sequence. The consistency index of the tree is 0.63. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Chaisson MJ, Pevzner PA. Short read fragment assembly of bacterial genomes. Genome Res. 2008;18:324–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cummings CA, Bormann Chung CA, Fang R, Barker M, Brzoska PM, Williamson P, Whole-genome typing of Bacillus anthracis isolates by next-generation sequencing accurately and rapidly identifies strain-specific diagnostic polymorphisms. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2009;2:300–1. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Harris SR, Feil EJ, Holden MT, Quail MA, Nickerson EK, Chantratita N, Evolution of MRSA during hospital transmission and intercontinental spread. Science. 2010;327:469–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Galgiani JN, Ampel NM, Blair Je, Catanzaro A. Johnson RH, Stevens DA, et al. Coccidioidomycosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1217–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Blair JE. Coccidioidomycosis in patients who have undergone transplantation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1111:365–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- The Broad Institute Coccidioides Group [updated 2010 Mar 31] [cited 2010 Apr 1]. http://www.broadinstitute.org/annotation/genome/coccidioides_group/GenomeDescriptions.html#iCoccidioidesimmitisiRS
- Homer N, Merriman B, Nelson SF. BFAST: an alignment tool for large scale genome resequencing. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e7767. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sharpton TJ, Stajich JE, Rounsley SD, Gardner MJ, Wortman JR, Jordar VS, Comparative genomic analyses of the human fungal pathogens Coccidioides and their relatives. Genome Res. 2009;19:1722–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Colvin SNP. Caller–TGen [updated 2010 Mar 31] [cited 2010 Apr 1]. http://public.tgen.org/merge-pileup
- Short Read Archive–NCBI [updated 2008 Nov 5] [cited 2010 Feb 15]. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/SRX022538?report=full
- Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The sequence alignment/map (SAM) format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:2078–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kurtz S, Phillippy A, Delcher A, Smoot M, Shumway M, Antonescu C, Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol. 2004;5:R12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1596–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nei M, Kumar S. Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. New York: Oxford University Press; 2000. p. 132.
- Keckich DW, Blair JE, Vikram HR. Coccidioides fungemia in six patients, with a review of the literature. Mycopathologia. 2010;170:107–15. Epub 2010 Mar 25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taylor JW, Geiser DM, Burt A, Koufopanou V. The evolutionary biology and population genetics underlying fungal strain typing. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999;12:126–46.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fisher MC, Koenig GL, White TJ, San-Blas G, Negroni R, Alvarez IG, Biogeographic range expansion into South America by Coccidioides immitis mirrors New World patterns of human migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:4558–62. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jewell K, Cheshire R, Cage GD. Genetic diversity among clinical Coccidioides spp. isolates in Arizona. Med Mycol. 2008;46:449–55. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Keim P, Van Ert M, Pearson T, Vogler A, Hyunh L, Wagner D. Anthrax molecular epidemiology and forensics: using different markers for the appropriate evolutionary scales. Infect Genet Evol. 2004;4:205–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pearson T, Okinaka RT, Foster JT, Keim P. Phylogenetic understanding of clonal populations in an era of whole genome sequencing. Infect Genet Evol. 2009;9:1010–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pearson T, Giffard P, Beckstrom-Sternberg S, Auerbach R, Hornstra H, Tuanyok A, Phylogeographic reconstruction of a bacterial species with high levels of lateral gene transfer BMC Biol. 2009; 18;7:78. PMID: 19922616
- Burt A, Carter DA, Koenig GL, White TJ, Taylor JW. Molecular markers reveal cryptic sex in the human pathogen Coccidioides immitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:770–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Greub G, Kebbi-Beghdadi C, Bertelli C, Collyn F, Riederer BM, Yersin C, High throughput sequencing and proteomics to identify immunogenic proteins of a new pathogen: the dirty genome approach. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e8423. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schielke A, Sachs K, Lierz M, Appel B, Jansen A, Johne R. Detection of hepatitis E virus in wild boars of rural and urban regions in Germany and whole genome characterization of an endemic strain. Virol J. 2009;14;6:58. PMID: 19442307
- Sanabani SS, Pastena ER, Kleine Neto W, Barreto CC, Ferrari KT, Kalmar EM, Near full-length genome analysis of low prevalent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subclade F1 in São Paulo, Brazil. Virol J. 2009;16;6:78. PMID: 19531216
- Liu J, Xiao H, Lei F, Zhu Q, Qin K, Zhang XW, Highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus infection in migratory birds. Science. 2005;309:1206. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Craig DW, Pearson JV, Szelinger S, Sekar A, Redman M, Corneveaux JJ, Identification of genetic variants using bar-coded multiplexed sequencing. Nat Methods. 2008;5:887–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009;10:R25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schatz MC. CloudBurst: highly sensitive read mapping with MapReduce. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1363–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Langmead B, Schatz MC, Lin J, Pop M, Salzberg SL. Searching for SNPs with cloud computing. Genome Biol. 2009;10:R134. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar