Volume 17, Number 2—February 2011
Dispatch
Oseltamivir-Resistant Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Virus, Mexico
Figure 2
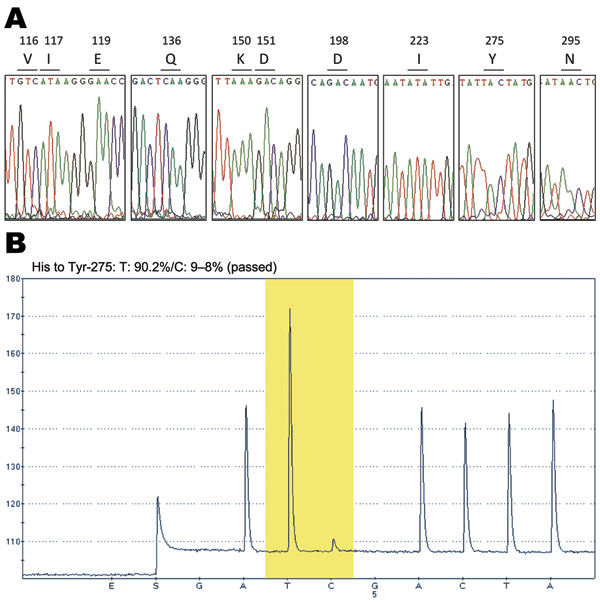
Figure 2. DNA sequence electropherograms for neuraminidase (NA) gene sequences. A) Analysis of molecular markers (V116, I117, E119, Q136, K150, D151, D198, I223, H275, and N295) for oseltamivir and/or zanamivir resistance among the pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus isolates. The oseltamivir resistance–conferring mutation CAC (histidine) to TAC (tyrosine) at position 275 was detected in the InDRE797 sample. B) Detection of the H275Y mutation in the NA of the viruses by single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis at NA275 position (yellow area).
Page created: July 13, 2011
Page updated: July 13, 2011
Page reviewed: July 13, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.