Volume 17, Number 2—February 2011
Research
Possible Increased Pathogenicity of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Influenza Virus upon Reassortment
Figure 3
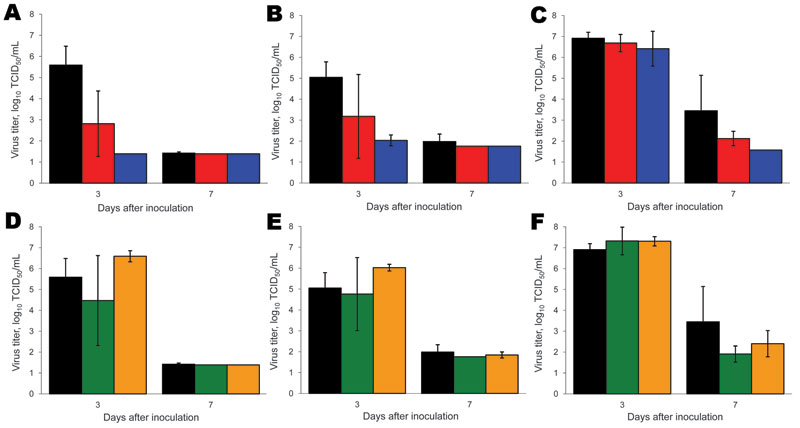
Figure 3. Virus detection in respiratory tissues of ferrets inoculated with wild-type and reassortant pandemic (H1N1) 2009 viruses. Virus detection in lungs (A, D), trachea (B, E), and nasal turbinates (C, F) is shown for pandemic (H1N1) 2009–seasonal influenza (H1N1) (A–C) and pandemic (H1N1) 2009–seasonal influenza (H3N2) (D–F) reassortant viruses. Black, wild-type pandemic (H1N1) 2009; red, pandemic (H1N1) 2009–seasonal influenza (H1N1) basic polymerase (PB) 2 acidic polymerase; blue, pandemic (H1N1) 2009–seasonal influenza (H1N1) PB2; green, pandemic (H1N1) 2009–seasonal influenza (H3N2) PB1 neuraminidase (NA); orange, pandemic (H1N1)–seasonal influenza (H3N2) NA. Three ferrets of each group were euthanized at 3 and 7 days postinoculation. Geometric mean titers are shown; error bars indicate SD. The lower limit of detection is 0.5 log10 50% tissue culture infective dose/mL (TCID50/mL).