Volume 17, Number 5—May 2011
Dispatch
Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus, Kyrgyzstan
Figure 2
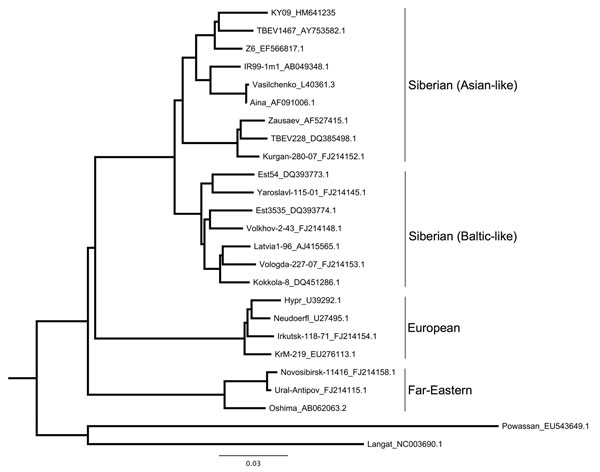
Figure 2. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of relationship between various tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) strains isolated from rodents, insectivores, and ticks, Kyrgyzstan, 2007 and 2009. Tree is based on partial sequencing of the envelope protein (from Cys3 to Gly286). Strain names are followed by GenBank accession numbers. The strain from Ala-Archa (KY09_HM641235) is most closely related to strains from Novosibirsk (TBEV 1467 and Z6). This strain was isolated from an Ixodes persulcatus tick pool, representative of 5 other positive tick pools, and from liver samples from 2 Apodemus pallipes mice (sequence analysis of other samples not shown). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
Page created: August 08, 2011
Page updated: August 08, 2011
Page reviewed: August 08, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.