Volume 17, Number 5—May 2011
Research
Evolution of New Genotype of West Nile Virus in North America
Figure 1
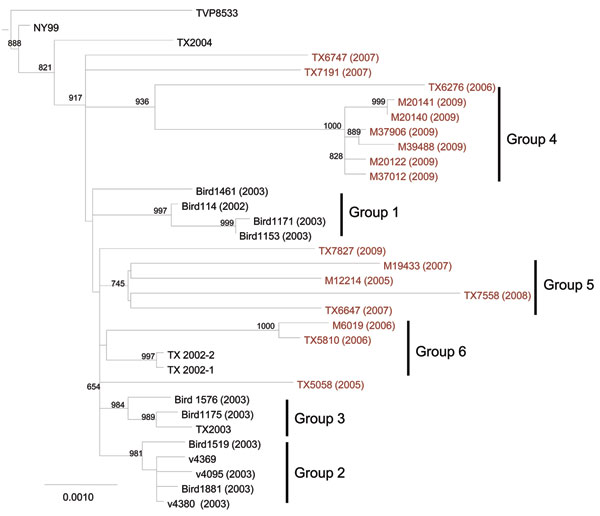
Figure 1. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of Upper Texas Gulf Coast, USA, West Nile virus isolates, 2002–2009. The tree was inferred from open reading frame sequences of 33 Upper Texas Gulf Coast isolates and NY99 by using PhyML (17) and rooted with IS-98 STD. The outgroup has been removed. Bootstrap values are for 1,000 replicates and only values >500 are shown. Groups 1–3 were previously identified by May et al. (12). Red, isolates sequenced in this study. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Hayes EB, Gubler DJ. West Nile virus: epidemiology and clinical features of an emerging epidemic in the United States. Annu Rev Med. 2006;57:181–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Le Guenno B, Bougermouh A, Azzam T, Bouakaz R. West Nile: a deadly virus? Lancet. 1996;348:1315. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lvov DK, Butenko AM, Gromashevsky VL, Larichev VP, Gaidamovich SY, Vyshemirsky OI, Isolation of two strains of West Nile virus during an outbreak in southern Russia, 1999. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6:373–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tsai TF, Popovici F, Cernescu C, Campbell GL, Nedelcu NI. West Nile encephalitis epidemic in southeastern Romania. Lancet. 1998;352:767–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Davis CT, Ebel GD, Lanciotti RS, Brault AC, Guzman H, Siirin M, Phylogenetic analysis of North American West Nile virus isolates, 2001–2004: evidence for the emergence of a dominant genotype. Virology. 2005;342:252–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ebel GD, Carricaburu J, Young D, Bernard KA, Kramer LD. Genetic and phenotypic variation of West Nile virus in New York, 2000–2003. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;71:493–500.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Moudy RM, Meola MA, Morin LL, Ebel GD, Kramer LD. A newly emergent genotype of West Nile virus is transmitted earlier and more efficiently by Culex mosquitoes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;77:365–70.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vanlandingham DL, McGee CE, Klingler KA, Galbraith SE, Barrett ADT, Higgs S. Comparison of oral infectious dose of West Nile virus isolates representing three distinct genotypes in Culex quinquefasciatus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008;79:951–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Beasley DW, Davis CT, Guzman H, Vanlandingham DL, Travassos da Rosa AP, Parsons RE, Limited evolution of West Nile virus has occurred during its southwesterly spread in the United States. Virology. 2003;309:190–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Davis CT, Beasley DW, Guzman H, Siirin M, Parsons RE, Tesh RB, Emergence of attenuated West Nile virus variants in Texas, 2003. Virology. 2004;330:342–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Davis CT, Galbraith SE, Zhang S, Whiteman MC, Li L, Kinney RM, A combination of naturally occurring mutations in North American West Nile virus nonstructural protein genes and in the 3′ untranslated region alters virus phenotype. J Virol. 2007;81:6111–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- May FJ, Li L, Davis CT, Galbraith SE, Barrett ADT. Multiple pathways to the attenuation of West Nile virus in south-east Texas in 2003. Virology. 2010;405:8–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Davis CT, Li L, May FJ, Bueno R Jr, Dennett JA, Bala AA, Genetic stasis of dominant West Nile virus genotype, Houston, Texas. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:601–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Snapinn KW, Holmes EC, Young DS, Bernard KA, Kramer LD, Ebel GD. Declining growth rate of West Nile virus in North America. J Virol. 2007;81:2531–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gouy M, Guindon S, Gascuel O. SeaView Version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol Biol Evol. 2010;27:221–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Felsenstein J. PHYLIP–Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2). Cladistics. 1989;5:164–6.
- Guindon S, Gascuel O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol. 2003;52:696–704. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Posada D, Crandall KA. MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics. 1998;14:817–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Swofford DL. PAUP*: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods). Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 1998.
- Kosakovsky Pond SL, Posada D, Gravenor MB, Woelk CH, Frost SD. Automated phylogenetic detection of recombination using a genetic algorithm. Mol Biol Evol. 2006;23:1891–901. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Delport W, Poon AFY, Frost SD, Kosakovsky Pond SL. Datamonkey 2010: a suite of phylogenetic analysis tools for evolutionary biology. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:2455–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pond SLK, Frost SDW. Datamonkey: rapid detection of selective pressure on individual sites of codon alignments. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:2531–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kosakovsky Pond SL, Frost SD. Not so different after all: a comparison of methods for detecting amino acid sites under selection. Mol Biol Evol. 2005;22:1208–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Poon AF, Kosakovsky Pond SL, Bennett P, Richman DD, Leigh Brown AJ, Frost SDW. Adaptation to human populations is revealed by within-host polymorphisms in HIV-1 and hepatitis C virus. PLoS Pathog. 2007;3:e45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series. 1999;41:95–8.
- Grinev A, Daniel S, Stramer S, Rossmann S, Caglioti S, Rios M. Genetic variability of West Nile virus in US blood donors, 2002–2005. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:436–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Herring BL, Bernardin F, Caglioti S, Stramer S, Tobler L, Andrews W, Phylogenetic analysis of WNV in North American blood donors during the 2003–2004 epidemic seasons. Virology. 2007;363:220–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Deardorff E, Estrada-Franco J, Brault AC, Navarro-Lopez R, Campomanes-Cortes A, Paz-Ramirez P, Introductions of West Nile virus strains to Mexico. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:314–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tang Y, Liu B, Hapip CA, Xu D, Fang CT. Genetic analysis of West Nile virus isolates from US blood donors during 2002–2005. J Clin Virol. 2008;43:292–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lanciotti RS, Ebel GD, Deubel V, Kerst AJ, Murri S, Meyer R, Complete genome sequences and phylogenetic analysis of West Nile virus strains isolated from the United States, Europe, and the Middle East. Virology. 2002;298:96–105. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bertolotti L, Kitron U, Goldberg TL. Diversity and evolution of West Nile virus in Illinois and the United States, 2002–2005. Virology. 2007;360:143–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bertolotti L, Kitron UD, Walker ED, Ruiz MO, Brawn JD, Loss SR, Fine-scale genetic variation and evolution of West Nile virus in a transmission “hot spot” in suburban Chicago, USA. Virology. 2008;374:381–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Amore G, Bertolotti L, Hamer GL, Kitron UD, Walker ED, Ruiz MO, Multi-year evolutionary dynamics of West Nile virus in suburban Chicago, USA, 2005–2007. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2010;365:1871–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brault AC, Huang CY, Langevin SA, Kinney RM, Bowen RA, Ramey WN, A single positively selected West Nile viral mutation confers increased virogenesis in American crows. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1162–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: August 14, 2011
Page updated: August 14, 2011
Page reviewed: August 14, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.