Volume 17, Number 6—June 2011
Letter
Swine Influenza Virus A (H3N2) Infection in Human, Kansas, USA, 2009
Appendix
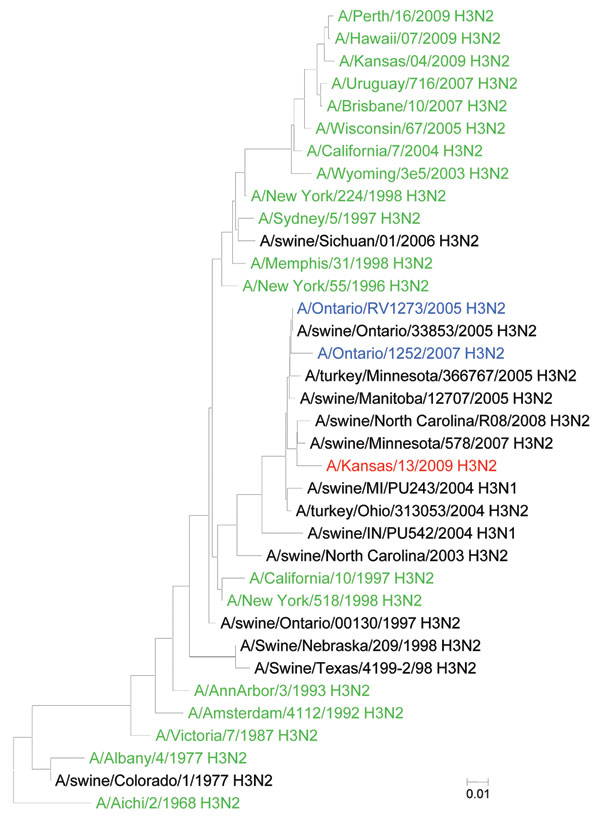
Appendix. Figure. Phylogenetic tree of the hemagglutinin (HA) gene segment of influenza A (H3) viruses created by using the neighbor-joining method, nucleotide model of Kimura-2 parameters, in MEGA version 4 (10). In addition, a subset of H3 HA gene sequences available in the public domain was included in the analyses for comparison. Red, A/Kansas/13/2009 (H3N2); green, human (H3N2) viruses; black, animal (H3N2) viruses; blue, human cases of swine (H3N2) viruses.
References
- Karasin AI, Schutten MM, Cooper LA, Smith CB, Subbarao K, Anderson GA, Genetic characterization of H3N2 influenza viruses isolated from pigs in North America, 1977–1999: evidence for wholly human and reassortant virus genotypes. Virus Res. 2000;68:71–85. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Newman AP, Reisdorf E, Beinemann J, Uyeki TM, Balish A, Shu B, Human case of swine influenza A (H1N1) triple reassortant virus infection, Wisconsin. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:1470–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Olsen CW, Karasin AI, Carman S, Li Y, Bastien N, Ojkic D, Triple reassortant H3N2 influenza A viruses, Canada, 2005. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1132–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shinde V, Bridges CB, Uyeki TM, Shu B, Balish A, Xu X, Triple-reassortant swine influenza A (H1) in humans in the United States, 2005–2009. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2616–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Robinson JL, Lee BE, Patel J, Bastien N, Grimsrud K, Seal RF, Swine influenza (H3N2) infection in a child and possible community transmission, Canada. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1865–70.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wells DL, Hopfensperger DJ, Arden NH, Harmon MW, Davis JP, Tipple MA, Swine influenza virus infections. Transmission from ill pigs to humans at a Wisconsin agricultural fair and subsequent probable person-to-person transmission. JAMA. 1991;265:478–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Top FH Jr, Russell PK. Swine influenza A at Fort Dix, New Jersey (January–February 1976). IV. Summary and speculation. J Infect Dis. 1977;136(Suppl):S376–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Garten RJ, Davis CT, Russell CA, Shu B, Lindstrom S, Balish A, Antigenic and genetic characteristics of swine-origin 2009 A(H1N1) influenza viruses circulating in humans. Science. 2009;325:197–201. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. CDC protocol of real-time RTPCR for influenza A (H1N1). 2009 April 30, 2009 [cited 2010 July 6]; http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/swineflu/realtimeptpcr/en/index.html
- Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1596–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: August 03, 2011
Page updated: August 03, 2011
Page reviewed: August 03, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.