Volume 17, Number 6—June 2011
Dispatch
Worldwide Distribution of Major Clones of Listeria monocytogenes
Figure A1
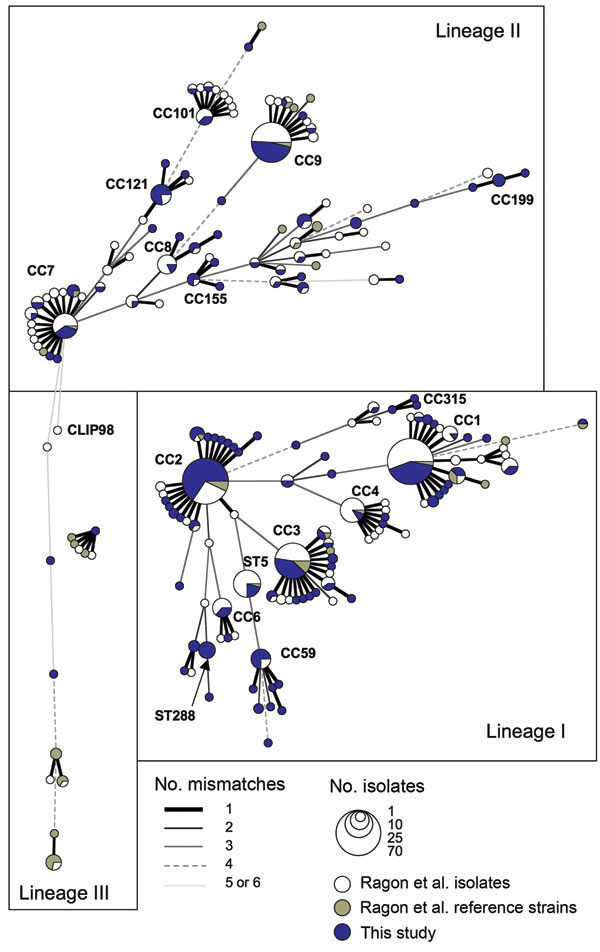
Figure A1. Genetic relationships among 660 Listeria monocytogenes isolates. The graph is a minimum spanning tree based on allelic profiles by using BioNumerics version 6.1 (Applied-Maths, Sint-Martens-Latem, Belgium). The 300 isolates of this study are in blue; the 360 L. monocytogenes isolates and reference strains of our earlier study (12) are in white and gray, respectively. Each circle represents a multilocus sequence typing genotype (ST), the size of which is related to the number of isolates (see legend). Clones, defined as clonal complexes [CC], are composed of groups of STs linked with a single gene difference, denoted as bold lines (see legend); clone number is indicated for the major clones. Links with >2 mismatches are unreliable because many alternatives may exist; links with 7 mismatches are not shown.
References
- Denny J, McLauchlin J. Human Listeria monocytogenes infections in Europe—an opportunity for improved European surveillance. Euro Surveill. 2008;13:pii:8082.
- Goulet V, Hedberg C, Le Monnier A, de Valk H. Increasing incidence of listeriosis in France and other European countries. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:734–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Piffaretti JC, Kressebuch H, Aeschbacher M, Bille J, Bannerman E, Musser JM, Genetic characterization of clones of the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes causing epidemic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86:3818–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wiedmann M, Bruce JL, Keating C, Johnson AE, McDonough PL, Batt CA. Ribotypes and virulence gene polymorphisms suggest three distinct Listeria monocytogenes lineages with differences in pathogenic potential. Infect Immun. 1997;65:2707–16.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kathariou S. Listeria monocytogenes virulence and pathogenicity, a food safety perspective. J Food Prot. 2002;65:1811–29.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Evans MR, Swaminathan B, Graves LM, Altermann E, Klaenhammer TR, Fink RC, Genetic markers unique to Listeria monocytogenes serotype 4b differentiate epidemic clone II (hot dog outbreak strains) from other lineages. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004;70:2383–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ward TJ, Usgaard T, Evans P. A targeted multilocus genotyping assay for lineage, serogroup, and epidemic clone typing of Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76:6680–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lomonaco S, Chen Y, Knabel SJ. Analysis of additional virulence genes and virulence gene regions in Listeria monocytogenes confirms the epidemiologic relevance of multi-virulence-locus sequence typing. J Food Prot. 2008;71:2559–66.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- den Bakker HC, Fortes ED, Wiedmann M. Multilocus sequence typing of outbreak-associated Listeria monocytogenes isolates to identify epidemic clones. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010;7:257–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kathariou S. Foodborne outbreaks of listeriosis and epidemic-associated lineages of Listeria monocytogenes. In: Torrence ME, Isaacson RE, editors. Microbial food safety in animal agriculture. Ames (IA): Iowa State University Press; 2003. p. 243–56.
- Chen Y, Zhang W, Knabel SJ. Multi-virulence-locus sequence typing identifies single nucleotide polymorphisms which differentiate epidemic clones and outbreak strains of Listeria monocytogenes. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:835–46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ragon M, Wirth T, Hollandt F, Lavenir R, Lecuit M, Le Monnier A, A new perspective on Listeria monocytogenes evolution. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4:e1000146. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Doumith M, Buchrieser C, Glaser P, Jacquet C, Martin P. Differentiation of the major Listeria monocytogenes serovars by multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:3819–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Martiny JB, Bohannan BJ, Brown JH, Colwell RK, Fuhrman JA, Green JL, Microbial biogeography: putting microorganisms on the map. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2006;4:102–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pirnay JP, Matthijs S, Colak H, Chablain P, Bilocq F, Van Eldere J, Global Pseudomonas aeruginosa biodiversity as reflected in a Belgian river. Environ Microbiol. 2005;7:969–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this study.
2These authors contributed equally to this study.