Volume 17, Number 7—July 2011
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Neurognathostomiasis, a Neglected Parasitosis of the Central Nervous System
Figure 2
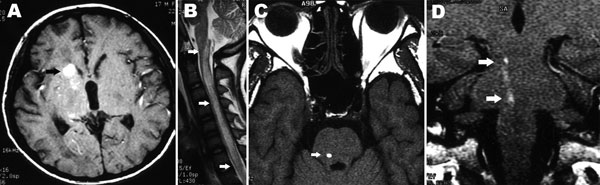
Figure 2. Images of the brains of patients with cerebral gnathostomiasis. A) Axial T1-weighted image showing small hemorrhage in the right basal ganglia (arrow). B) Sagittal T2-weighted images showing diffuse cord enlargement with longitudinal T2 hyperintensity (arrows). C) Axial T1-weighted image showing a hemorrhagic track in the tegmentum of the pons (arrow). D) Coronal T1-weighted postgadolinium image, showing the longitudinal extension of the same hemorrhagic track as in panel C (arrows). Images from K. Sawanyawisuth et al. (11), used with permission.
References
- Nawa Y, Hatz C, Blum J. Sushi delights and parasites: the risk of fishborne and foodborne parasitic zoonoses in Asia. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1297–303. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Moore DA, McCroddan J, Dekumyoy P, Chiodini PL. Gnathostomiasis: an emerging imported disease. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:647–50.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nawa Y. Historical review and current status of gnathostomiasis in Asia. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1991;22(Suppl):217–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Herman JS, Chiodini PL. Gnathostomiasis, another emerging imported disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009;22:484–92. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rusnak JM, Lucey DR. Clinical gnathostomiasis: case report and review of the English-language literature. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;16:33–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chai JY, Han ET, Shin EH, Park JH, Chu JP, Hirota M, An outbreak of gnathostomiasis among Korean emigrants in Myanmar. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;69:67–73.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Daengsvang S. Human gnathostomiasis in Siam with reference to the method of prevention. J Parasitol. 1949;35:116–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chitanondh H, Rosen L. Fatal eosinophilic encephalomyelitis caused by the nematode Gnathostoma spinigerum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967;16:638–45.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boongird P, Phuapradit P, Siridej N, Chirachariyavej T, Chuahirun S, Vejjajiva A. Neurological manifestations of gnathostomiasis. J Neurol Sci. 1977;31:279–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Punyagupta S, Bunnag T, Juttijudata P. Eosinophilic meningitis in Thailand. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of 162 patients with myeloencephalitis probably caused by Gnathostoma spinigerum. J Neurol Sci. 1990;96:241–56. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sawanyawisuth K, Tiamkao S, Kanpittaya J, Dekumyoy P, Jitpimolmard S. MR imaging findings in cerebrospinal gnathostomiasis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:446–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brant-Zawadzki M, Wofsy CB, Schechter G. CT-evidence of subarachnoid hemorrhage due to presumed gnathostomiasis. West J Med. 1982;137:65–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Strady C, Dekumyoy P, Clement-Rigolet M, Danis M, Bricaire F, Caumes E. Long-term follow-up of imported gnathostomiasis shows frequent treatment failure. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009;80:33–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kawamura J, Kohri Y. Nobuyuki 0. Eosinophilic meningoradiculo-myelitis caused by Gnathostoma spinigerum: a case report. Arch Neurol. 1983;40:583–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lo Re V III, Gluckman SJ. Eosinophilic meningitis due to Gnathostoma spinigerum. J Infect. 2002;45:117–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Catalano M, Kaswan D, Levi MH. Wider range for parasites that cause eosinophilic meningitis. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:1283. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chandenier J, Husson J, Canaple S, Gondry-Jouet C, Dekumyoy P, Danis M, Medullary gnathostomiasis in a white patient: use of immunodiagnosis and magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:E154–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Germann R, Schächtele M, Nessler G, Seitz U, Kniehl E. Cerebral gnathostomiasis as a cause of an extended intracranial bleeding. Klin Padiatr. 2003;215:223–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Górgolas M, Santos-O'Connor F, Unzú AL, Fernández-Guerrero ML, Gárate T, Troyas Guarch RM, Cutaneous and medullar gnathostomiasis in travelers to Mexico and Thailand. J Travel Med. 2003;10:358–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Elzi L, Decker M, Battegay M, Rutishauser J, Blum J. Chest pain after travel to the tropics. Lancet. 2004;363:1198. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schmutzhard E. Eosinophilic myelitis, a souvenir from South East Asia. Pract Neurol. 2007;7:48–51.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Herman JS, Wall EC, van-Tulleken C, Godfrey-Faussett P, Bailey RL, Chiodini PL. Gnathostomiasis acquired by British tourists in Botswana. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:594–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hale DC, Blumberg L, Frean J. Case report: gnathostomiasis in two travelers to Zambia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68:707–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Katchanov J, Nawa Y. Helminthic invasion of the central nervous system: many roads lead to Rome. Parasitol Int. 2010;59:491–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maruyama H, Nawa Y. Immunology of the infection. In: Murrell KD, Fried B, editors. Worldclass parasites, vol. 11, food-borne parasitic zoonoses. Fish and plant-borne parasites. New York: Springer; 2007. p. 337–81.
- Tort J, Brindley PJ, Knox D, Wolfe KH, Dalton JP. Proteinases and associated genes of parasitic helminths. Adv Parasitol. 1999;43:161–266. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Uparanukraw P, Morakote N, Harnnoi T, Dantrakool A. Molecular cloning of a gene encoding matrix metalloproteinase-like protein from Gnathostoma spinigerum. Parasitol Res. 2001;87:751–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Punyagupta S, Limtrakul C, Vichipanthu P, Karnchanachetanee C, Nye SW. Radiculomyeloencephalitis associated with eosinophilic pleocytosis—report of nine cases. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968;17:551–60.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sawanyawisuth K, Chlebicki MP, Pratt E, Kanpittaya J, Intapan PM. Sequential imaging studies of cerebral gnathostomiasis with subdural hemorrhage as its complication. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2009;103:102–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rojekittikhun W, Pubampen S. Morphological variation and abnormality of cephalic hooklets of Gnathostoma spinigerum hepatic stage larvae from laboratory infected mice. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1998;29:118–22.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sithinamsuwan P, Chairangsaris P. Images in clinical medicine. Gnathostomiasis—neuroimaging of larval migration. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:188. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Visudhiphan P, Chiemchanya S, Somburanasin R, Dheandhanoo D. Causes of spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage in Thai infants and children. A study of 56 patients. J Neurosurg. 1980;53:185–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schmutzhard E, Boongird P, Vejjajiva A. Eosinophilic meningitis and radiculomyelitis in Thailand, caused by CNS invasion of Gnathostoma spinigerum and Angiostrongylus cantonensis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988;51:80–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Punyagupta S, Juttijudata P, Bunnag T, Comer DS. Two fatal cases of eosinophilic myeloencephalitis a newly recognized disease caused by Gnathostoma spinigerum. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62:801–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bunyaratavej K, Pongpunlert W, Jongwutiwes S, Likitnukul S. Spinal gnathostomiasis resembling an intrinsic cord tumor/myelitis in a 4-year-old boy. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2008;39:800–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bunnag T, Comer DS, Punyagupta S. Eosinophilic myeloencephalitis caused by Gnathostoma spinigerum. Neuropathology of nine cases. J Neurol Sci. 1970;10:419–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Daengsvang S. A monograph on the genus Gnasthostoma and gnathostomiasis in Thailand. Tokyo: Southeast Asian Medical Information Center International Medical Foundation of Japan; 1980.
- Sawanyawisuth K, Tiamkao S, Nitinavakarn B, Dekumyoy P, Jitpimolmard S. MR imaging findings in cauda equina gnathostomiasis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26:39–42.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Laummaunwai P, Sawanyawisuth K, Intapan PM, Chotmongkol V, Wongkham C, Maleewong W. Evaluation of human IgG class and subclass antibodies to a 24 kDa antigenic component of Gnathostoma spinigerum for the serodiagnosis of gnathostomiasis. Parasitol Res. 2007;101:703–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Eamsobhana P, Ongrotchanakun J, Yookek A, Punthuprapasa P, Monkong N, Dekumyoy P. Multi-immunodot for rapid differential diagnosis of eosinophilic meningitis due to parasitic infections. J Helminthol. 2006;80:249–54.PubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: August 16, 2011
Page updated: August 16, 2011
Page reviewed: August 16, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.