Volume 17, Number 7—July 2011
Dispatch
Clonal Genotype of Geomyces destructans among Bats with White Nose Syndrome, New York, USA
Figure 1
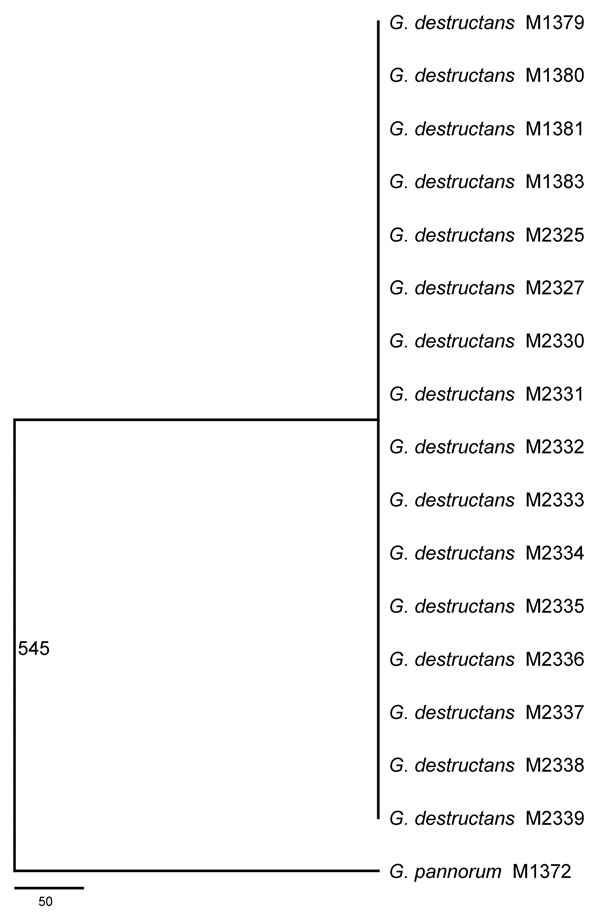
Figure 1. Consensus maximum-parsimony tree derived from analyzing 8 concatenated gene fragments including a total of 4,470 aligned nucleotides by using PAUP* 4.0 (8). The number 545 on the branch indicates the total number of variable nucleotide positions (out of the 4,470 nt) separating Geomyces pannorum M1372 from the clonal genotype of G. destructans identified here. Fifty of the 545 variable sites correspond to insertions and deletions. Scale bar indicates number of nucleotide substitutions per site.
Page created: August 18, 2011
Page updated: August 18, 2011
Page reviewed: August 18, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.