Volume 17, Number 9—September 2011
Research
Differential Effects of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 on Remote and Indigenous Groups, Northern Territory, Australia, 2009
Figure 2
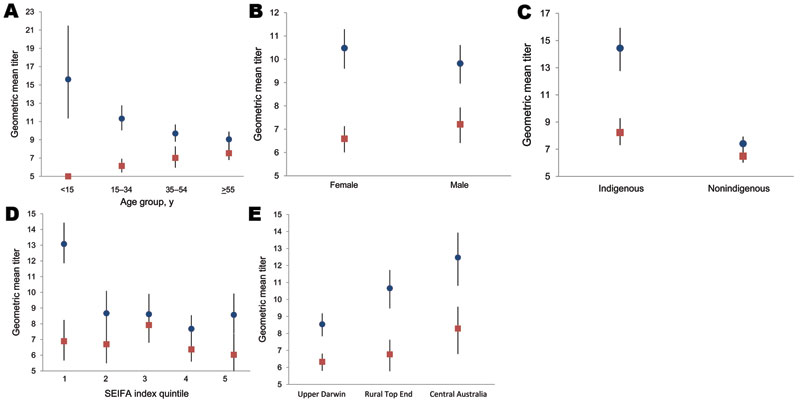
Figure 2. Unadjusted geometric mean antibody titers by age group (A), sex (B), indigenous status (C), SEIFA index (D), and study region (E) in a study of differential effects of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 on remote and indigenous groups, Northern Territory, Australia, September 2009. Red, prepandemic titer; blue, postpandemic titer. Bars indicate range. SEIFA, Australian Bureau of Statistics’ Socio-Economic Indexs for Area.
Page created: September 06, 2011
Page updated: September 06, 2011
Page reviewed: September 06, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.