Volume 17, Number 9—September 2011
CME ACTIVITY - Research
Mycobacterium chelonae-abscessus Complex Associated with Sinopulmonary Disease, Northeastern USA
Figure 6
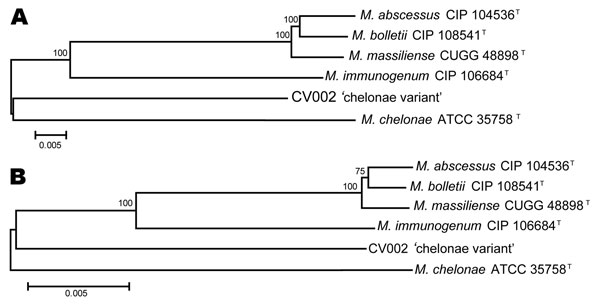
Figure 6. Neighbor-joining tree of DNA (A) and amino acid (B) concatenated gene sequences of Mycobacterium chelonae variant (CV) isolates and reference strains of the M. chelonae-abscessus complex. Branch support is recorded at nodes as a percentage of 1,000 bootstrap iterations. Upper scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site and lower scale bar indicates amino acid substitutions per site. CIP, Collection of Institute Pasteur; CCUG, Culture Collection, University of Göteborg, Sweden; CV, M. chelonae variant; ATCC, American Type Culture Collection.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: September 06, 2011
Page updated: September 06, 2011
Page reviewed: September 06, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.