Volume 17, Number 9—September 2011
Dispatch
Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Veterinary Clinics, Germany
Figure 1
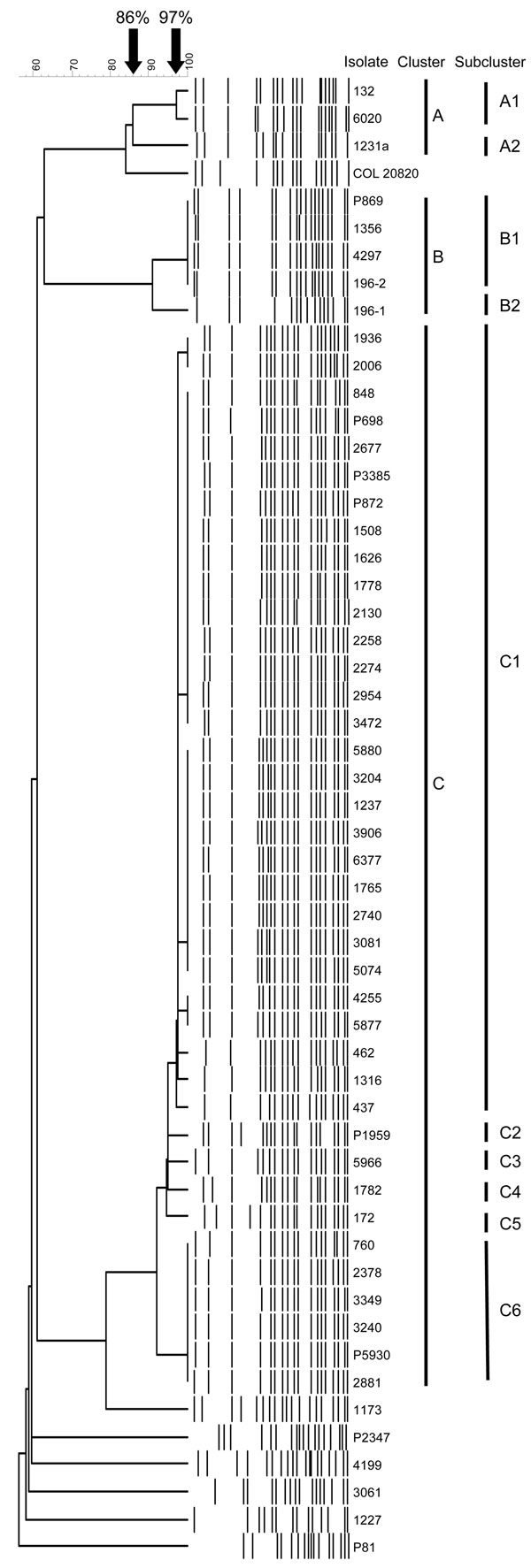
Figure 1. Computer-assisted cluster analysis of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis fingerprints of 53 Acinetobacter baumannii and 2 Acinetobacter spp. pittii isolates. COL 20820 was used as the reference standard for normalization of the digitized gels (14).
References
- Dijkshoorn L, Nemec A, Seifert H. An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5:939–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Peleg AY, Seifert H, Paterson DL. Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008;21:538–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maragakis LL, Perl TM. Acinetobacter baumannii: epidemiology, antimicrobial resistance, and treatment options. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:1254–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nemec A, Dijkshoorn L, van der Reijden TJ. Long-term predominance of two pan-European clones among multi-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains in the Czech Republic. J Med Microbiol. 2004;53:147–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dijkshoorn L, Aucken H, Gerner-Smidt P, Janssen P, Kaufmann ME, Garaizar J, Comparison of outbreak and nonoutbreak Acinetobacter baumannii strains by genotypic and phenotypic methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:1519–25.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Dessel H, Dijkshoorn L, van der Reijden T, Bakker N, Paauw A, van den Broek P, Identification of a new geographically widespread multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clone from European hospitals. Res Microbiol. 2004;155:105–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Abbott Y, O’Mahony R, Leonard N, Quinn PJ, van der Reijden T, Dijkshoorn L, Characterization of a 2.6 kbp variable region within a class 1 integron found in an Acinetobacter baumannii strain isolated from a horse. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;55:367–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Francey T, Gaschen F, Nicolet J, Burnens AP. The role of Acinetobacter baumannii as a nosocomial pathogen for dogs and cats in an intensive care unit. J Vet Intern Med. 2000;14:177–83.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance standards for antimicrobial disk and dilution susceptibility tests for bacteria isolated from animals, approved standard, 2nd ed. M31–A2. Wayne (PA): The Committee; 2002.
- Dijkshoorn L, Van Harsselaar B, Tjernberg I, Bouvet PJ, Vaneechoutte M. Evaluation of amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis for identification of Acinetobacter genomic species. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1998;21:33–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nemec A, Krizova L, Maixnerova M, Tanny der Reijden JK, Deschaght P, Passet V, Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus–Acinetobacter baumannii complex with the proposal of Acinetobacter pittii sp. nov. (formerly Acinetobacter genomic species 3) and Acinetobacter nosocomialis sp. nov. (formerly Acinetobacter genomic species 13TU). Res Microbiol. 2011;162:393–404. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van den Broek PJ, van der Reijden TJ, van Strijen E, Helmig-Schurter AV, Bernards AT, Dijkshoorn L. Endemic and epidemic acinetobacter species in a university hospital: an 8-year survey. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:3593–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dijkshoorn L. Typing Acinetobacter strains: applications and methods. In: Bergogne-Berezin E, Friedmann H, Bendinelli M, editors. Acinetobacter biology and pathogenesis. New York (NY): Springer Science+Business Media; 2008. p. 85–104.
- Seifert H, Dolzani L, Bressan R, van der Reijden T, van Strijen B, Stefanik D, Standardization and interlaboratory reproducibility assessment of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis-generated fingerprints of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:4328–35. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van den Broek PJ, Arends J, Bernards AT, De Brauwer E, Mascini EM, van der Reijden TJ, Epidemiology of multiple Acinetobacter outbreaks in the Netherlands during the period 1999–2001. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006;12:837–43. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: September 06, 2011
Page updated: September 06, 2011
Page reviewed: September 06, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.