Volume 17, Number 9—September 2011
Letter
Escherichia coli O104:H4 from 2011 European Outbreak and Strain from South Korea
Cite This Article
Citation for Media
To the Editor: Beginning in early May 2011, an outbreak caused by Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli O104:H4 was reported in Germany and other countries in Europe. In this outbreak, the number of hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) cases has been unusually high (1). As of June 9, 2011, a total of 722 cases of HUS, 19 deaths, and 2,745 cases of enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) infection were reported (2).
A case of HUS caused by E. coli O104:H4 was first reported in South Korea in 2004 (3). Because infections caused by E. coli O104:H4 have been reported rarely, interest has arisen in the E. coli O104:H4 strain from South Korea. We characterized the E. coli O104:H4 strain isolated in South Korea (EC0417119) in 2004 and compared it with the E. coli O104:H4 strain associated with the current EHEC outbreak in Europe.
The serotype EC0417119, isolated from a patient with HUS in 2004, was reconfirmed as E. coli O104:H4. The strain was positive for stx1 and stx2 by PCR (4) but negative for aggR by PCR (5). In the antimicrobial drug susceptibility test using VITEK 2 AST-N169 test kit (bioMérieux, Marcy L’Etoile, France), the strain was resistant to ampicillin, ampicillin/sulbactam, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole but susceptible to ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, nalidixic acid, and tetracycline.
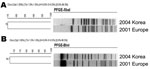
We also performed pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) for EC0417119, according to the PulseNet standard protocol (6), and compared its PFGE profile with that of the current outbreak strain E. coli O104:H4, which was obtained from the PulseNet Asia Pacific network. PFGE profiles resolved by either XbaI or BlnI did not match each other. The percentage similarity of XbaI- and BlnI-digested PFGE profiles of the 2 isolates was 75% and 66.7%, respectively, as shown in the Figure.
Infections with the EHEC O104 strain were reported several times worldwide. In Europe, such occurrence was rare, and before the current outbreak, the EHEC O104:H4 strain was documented only once in South Korea. For this reason, it was logical to examine the possible relatedness of the EC0417119 strain and the strain causing the current outbreak. However, the EC0417119 strain has many different characteristics compared with the current outbreak strain: not possessing enteroaggregative E. coli determinant, not producing extended-spectrum β-lactamases, and not showing indistinguishable PFGE patterns. In conclusion, there is no evidence that the E. coli O104:H4 strain isolated in South Korea in 2004 is related to the strain that has a caused the massive and unprecedented EHEC outbreak in Europe.
References
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. ECDC rapid risk assessment; outbreak of STEC in Germany [cited 27 May 2011]. http://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/Publications/1105_TER_Risk_assessment_EColi.pdf
- World Health Organization/Europe. International health regulations: EHEC outbreak [cited 2011 Jun 9]. http://www.euro.who.int/en/what-we-do/health-topics/emergencies/international-health-regulations/outbreaks-of-e.-coli-o104h4-infection
- Bae WK, Lee YK, Cho MS, Ma SK, Kim SW, Kim NH, A case of hemolytic uremic syndrome caused by Escherichia coli O104:H4. Yonsei Med J. 2006;47:437–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ito H, Terai A, Kurazono H, Takeda Y, Nishibuchi M. Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of vero toxin 2 variant genes from the Escherichia coli O91:H21 isolated from a patient with the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Microb Pathog. 1990;8:47–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weinstein DL, Jackson MP, Samuel JE, Holmes RK, O’Brien AD. Cloning and sequencing of a Shiga-like toxin type II variant from Escherichia coli strain responsible for edema disease of swine. J Bacteriol. 1988;170:4223–30.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- PulseNet International. PFGE protocols [cited 2011 Jun 29]. http://www.pulsenetinternational.org/protocols/Pages/default.aspx
Figure
Cite This ArticleRelated Links
Table of Contents – Volume 17, Number 9—September 2011
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Seonghan Kim, Division of Enteric Bacterial Infections, Center for Infectious Disease, National Institute of Health, Osong Health Technology Administration Complex, 643, Yeonje-ri, Gangoe-myeon, Cheonwon-gun, Chncheongbuk-do, South Korea 363-951
Top