Volume 18, Number 1—January 2012
Letter
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus in Ticks, Southwestern Europe, 2010
Figure
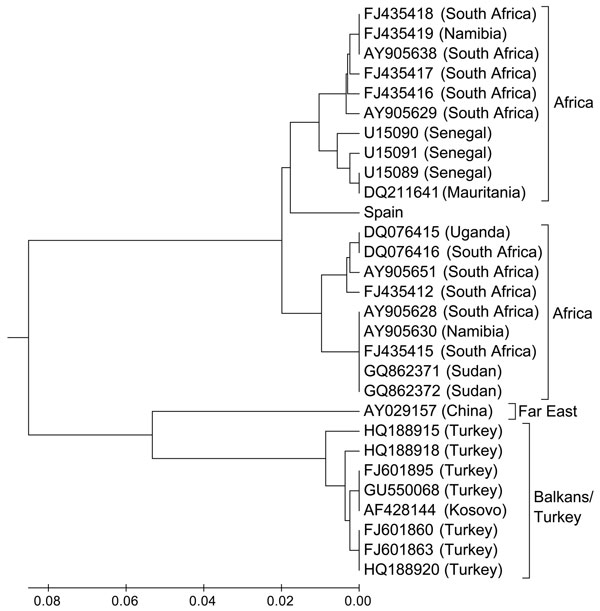
Figure. Evolutionary relationships of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus strains from Spain and other representative sites. Evolutionary history was inferred by using the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean. The optimal tree is shown (sum of branch length, 0.36861921). The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. Evolutionary distances were computed by using the maximum composite likelihood method and are in the units of the no. of base substitutions per site. Analysis involved 29-nt sequences. The first, second, third, and noncoding codon positions were included. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. Evolutionary analyses were conducted by using MEGA5 (www.megasoftware.net).