Volume 18, Number 11—November 2012
Research
Lack of Cross-protection against Bordetella holmesii after Pertussis Vaccination
Figure 4
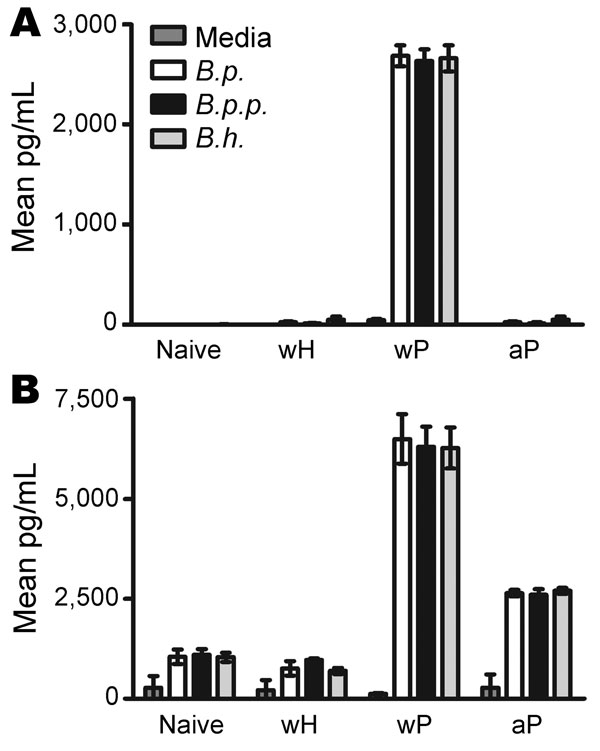
Figure 4. . . . Comparison of splenic interferon (IFN)–γ (A) and interleukin (IL)–10 (B) responses in naive mice versus mice vaccinated with whole-cell Bordetella holmesii vaccine (wH), whole-cell pertussis vaccine (wP), and acelullar pertussis vaccine (aP). Splenocytes from naive mice or wH-, wP-, or aP-vaccinated mice were stimulated with media only or media containing heat-killed B. pertussis (B.p.), B. parapertussis (B.p.p.), or B. holmesii (B.h.). Error bars indicate SE.
Page created: October 15, 2012
Page updated: October 15, 2012
Page reviewed: October 15, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.