Volume 18, Number 12—December 2012
Dispatch
Cygnet River Virus, a Novel Orthomyxovirus from Ducks, Australia
Figure 2
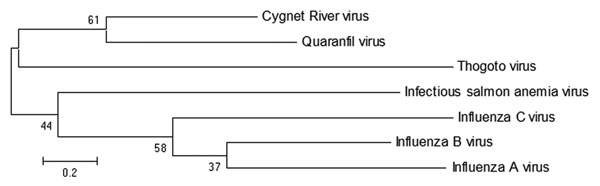
Figure 2. . Maximum-likelihood tree showing phylogenetic relationships between Cygnet River virus isolate 10–01646 (GenBank accession no. JQ693418) and other orthomyxoviruses: Quaranfil virus isolate EG T 377 (accession no. GQ499304), Thogoto virus strain PoTi503 (accession no. AF527530), infectious salmon anemia virus isolate RPC/NB (accession no. AF435424), influenza C virus C/Yamagata/8/96 (accession no. AB064433), influenza B virus B/Wisconsin/01/2010 (accession no. CY115184), and influenza A virus A/California/07/2009(H1N1) (accession no. CY121681). Tree was based on deduced amino acid sequences of the complete matrix protein of orthomyxoviruses, applying 1,000 bootstrap replicates (6). Numbers at nodes indicate percentage of 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Hawes P, Netherton CL, Mueller M, Wileman T, Monaghan P. Rapid freeze-substitution preserves membranes in high-pressure frozen tissue culture cells. J Microsc. 2007;226:182–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lozano ME, Posik DM, Albariño CG, Schujman G, Ghiringhelli PD, Calderón G, Characterization of arenaviruses using a family-specific primer set for RT-PCR amplification and RFLP analysis. Its potential use for detection of uncharacterized arenaviruses. Virus Res. 1997;49:79–89. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Smith I, Broos A, de Jong C, Zeddeman A, Smith C, Smith G, Identifying Hendra virus diversity in pteropid bats. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e25275. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–10 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Presti RM, Zhao G, Beatty WL, Mihindukulasuriya KA, Travassos da Rosa APA, Popov VL, Quaranfil, Johonston Atoll, and Lake Chad viruses are novel members of the family Orthomyxoviridae. J Virol. 2009;83:11599–606. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taylor RM, Hurlbut HS, Work TH, Kingston JR, Hoogstraal H. Arboviruses isolated from Argas ticks in Egypt: Quaranfil, Chenuda, and Nyamanini. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966;15:76–86 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zeller HG, Karabatsos N, Calisher CH, Digoutte JP, Murphy FA, Shope RA. Electron microscopy and antigenic studies of uncharacterized viruses. I. Evidence suggesting the placement of viruses in families Arenaviridae, Paramyxoviridae, or Poxviridae. Arch Virol. 1989;108:191–209. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barrette RW, Metwally SA, Rowland JM, Xu L, Zaki SR, Nichol ST, Discovery of swine as a host for the Reston ebolavirus. Science. 2009;325:204–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Current affiliation: Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, New South Wales, Australia.