Volume 18, Number 8—August 2012
Dispatch
Seroprevalence and Cross-reactivity of Human Polyomavirus 9
Figure 1
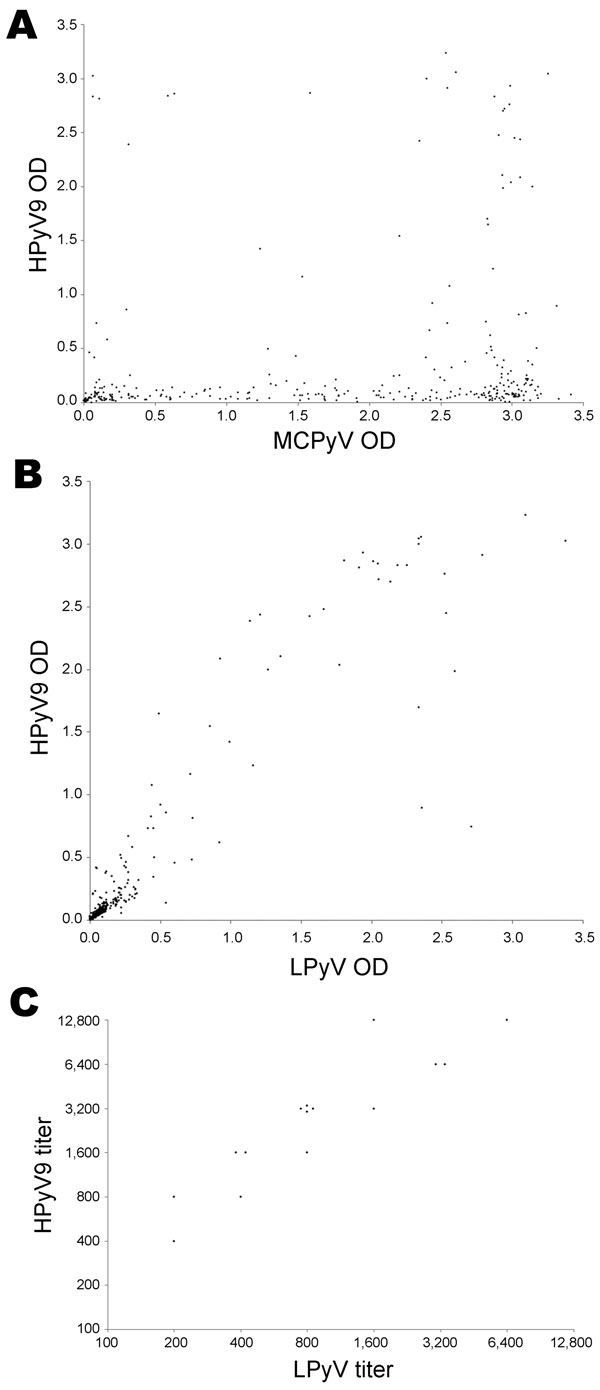
Figure 1. . Cross-reactivity between human polyomavirus 9 (HPyV9), simian lymphotropic polyomavirus (LPyV), and Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) virus–like particles (VLPs). Correlation between A) seroreactivity of 325 serum samples from children and adults in Italy against HPyV9 VLPs and B) MCPyV VLPs and HPyV9 VLPs was analyzed by ELISA. Each point represents 1 serum sample. Correlation coefficients (Spearman ρ) were determined by using XLStat software (Addinsoft, Paris, France). Correlation coefficient was 0.842 in panel B and 0.139 in panel A. C) Titers of 15 serum samples from adults against HPyV9 VLPs and LPyV VLPs. Each point represents 1 serum sample. OD, optical density.
Page created: July 23, 2012
Page updated: July 23, 2012
Page reviewed: July 23, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.