Volume 19, Number 11—November 2013
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Tropheryma whipplei Endocarditis
Figure 1
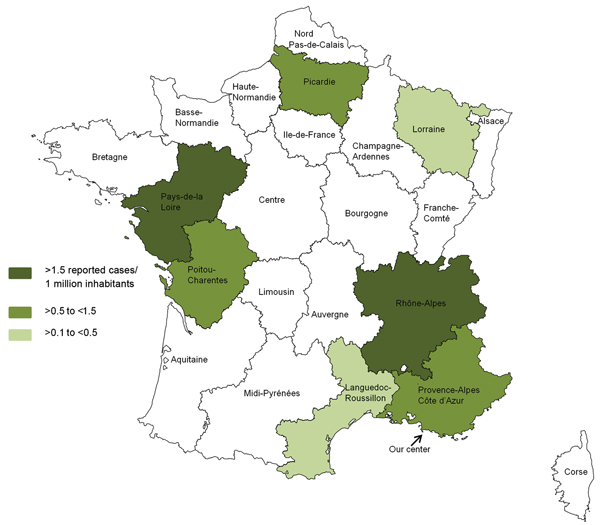
Figure 1. . . . . . Number of reported cases of Tropheryma whipplei endocarditis per 1 million inhabitants in each area of France over 10 years. Data from this series and the literature (22–24) were included. Among the metropolitan areas in France, the incidence of T. whipplei endocarditis is significantly more frequent in the Rhône-Alpes area than in 11 others areas (Alsace, Aquitaine, Basse-Normandie, Bourgogne, Centre, Champagne-Ardenne, Haute-Normandie, Ile de France, Languedoc-Roussillon, Midi-Pyrénées, and Nord Pas-de-Calais; p = 0.04, p = 0.004, p = 0.048, p = 0.04, p = 0.01, p = 0.04, p = 0.02, p<0.001, p = 0.04, p = 0.007, p = 0.006, respectively). The incidence rate is also significantly more frequent in the Pays de la Loire area than in 6 other areas (Aquitaine, Bretagne, Centre, Ile-de France, Lorraine, Midi-Pyrénées, Nord Pas de Calais; p = 0.04, p = 0.04, p = 0.04, p = 0.003, p = 0.03, p = 0.02, respectively).
References
- Moos V, Schneider T. Changing paradigms in Whipple’s disease and infection with Tropheryma whipplei. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011;30:1151–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lagier JC, Lepidi H, Raoult D, Fenollar F. Systemic Tropheryma whipplei: clinical presentation of 142 patients with infections diagnosed or confirmed in a reference center. Medicine (Baltimore). 2010;89:337–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Goldenberger D, Kunzli A, Vogt P, Zbinden R, Altwegg M. Molecular diagnosis of bacterial endocarditis by broad-range PCR amplification and direct sequencing. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:2733–9 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gubler JG, Kuster M, Dutly F, Bannwart F, Krause M, Vögelin HP, Whipple endocarditis without overt gastrointestinal disease: report of four cases. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131:112–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Raoult D, Birg M, La Scola B, Fournier P, Enea M, Lepidi H, Cultivation of the bacillus of Whipple's disease. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:620–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fournier PE, Thuny F, Richet H, Lepidi H, Casalta JP, Arzouni JP, Comprehensive diagnostic strategy for blood culture–negative endocarditis: a prospective study of 819 new cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:131–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Geissdörfer W, Moos V, Moter A, Loddenkemper C, Jansen A, Tandler R, High frequency of Tropheryma whipplei in culture-negative endocarditis. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:216–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Voldstedlund M, Norum PL, Baandrup U, Klaaborg KE, Fuursted K. Broad-range PCR and sequencing in routine diagnosis of infective endocarditis. APMIS. 2008;116:190–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bosshard PP, Kronenberg A, Zbinden R, Ruef C, Bottger EC, Altwegg M. Etiologic diagnosis of infective endocarditis by broad-range polymerase chain reaction: a 3-year experience. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37:167–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Grijalva M, Horvath R, Dendis M, Erny J, Benedik J. Molecular diagnosis of culture negative infective endocarditis: clinical validation in a group of surgically treated patients. Heart. 2003;89:263–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Marín M, Muñoz P, Sánchez M, del Rosal M, Alcalá L, Rodríguez-Créixems M, Molecular diagnosis of infective endocarditis by real-time broad-range polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequencing directly from heart valve tissue. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86:195–202. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Benslimani A, Fenollar F, Lepidi H, Raoult D. Bacterial zoonoses and infective endocarditis, Algeria. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:216–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fenollar F, Laouira S, Lepidi H, Rolain J, Raoult D. Value of Tropheryma whipplei quantitative PCR assay for the diagnosis of Whipple’s disease: usefulness of saliva and stool specimens for first-line screening. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:659–67. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li W, Fenollar F, Rolain JM, Fournier PE, Feurle GE, Müller C, Genotyping reveals a wide heterogeneity of Tropheryma whipplei. Microbiology. 2008;154:521–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lepidi H, Fenollar F, Dumler JS, Gauduchon V, Chalabreysse L, Bammert A, Cardiac valves in patients with Whipple endocarditis: microbiological, molecular, quantitative histologic, and immunohistochemical studies of 5 patients. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:935–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Raoult D, Fenollar F, Birg ML. Culture of Tropheryma whipplei from the stool of a patient with Whipple’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1503–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fenollar F, Amphoux B, Raoult D. A paradoxical Tropheryma whipplei Western blot differentiates patients with Whipple’s disease from asymptomatic carriers. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:717–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ansemant T, Celard M, Tavernier C, Maillefert JF, Delahaye F, Ornetti P. Whipple’s disease endocarditis following anti-TNF therapy for atypical rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2010;77:622–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Daïen CI, Cohen JD, Makinson A, Battistella P, Bilak EJ, Jorgensen C, Whipple’s endocarditis as a complication of tumour necrosis factor-alpha antagonist treatment in a man with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:1600–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li JS, Sexton DJ, Mick N, Nettles R, Fowler VG Jr, Ryan T, Proposed modifications to the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30:633–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thuny F, Grisoli D, Collart F, Habib G, Raoult D. Management of infective endocarditis: challenges and perspectives. Lancet. 2012;379:965–75. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Besnard S, Cady A, Flecher E, Fily F, Revest M, Arvieux C, Should we systematically perform central nervous system imaging in patients with Whipple’s endocarditis? Am J Med. 2010;123:962.e–4.
- Brondex A, Jobic Y. Infective endocarditis as the only manifestation of Whipple’s disease: an atypical presentation. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2012;61:61–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Saba M, Rollot F, Park S, Grimaldi D, Sicard D, Abad S, Whipple disease, initially diagnosed as sarcoidosis. Presse Med. 2005;34:1521–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lagier JC, Fenollar F, Lepidi H, Raoult D. Evidence of lifetime susceptibility to Tropheryma whipplei in patients with Whipple’s disease. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:1188–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Célard M, de Gevigney G, Mosnier S, Buttard P, Benito Y, Etienne J, Polymerase chain reaction analysis for diagnosis of Tropheryma whippelii infective endocarditis in two patients with no previous evidence of Whipple’s disease. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:1348–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chan V, Wang B, Veinot JP, Suh KN, Rose G, Desjardins M, Tropheryma whipplei aortic valve endocarditis without systemic Whipple’s disease. Int J Infect Dis. 2011;15:e804–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dreier J, Szabados F, von Herbay A, Kroger T, Kleesiek K. Tropheryma whipplei infection of an acellular porcine heart valve bioprosthesis in a patient who did not have intestinal Whipple’s disease. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:4487–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Escher R, Roth S, Droz S, Egli K, Altwegg M, Tauber MG. Endocarditis due to Tropheryma whipplei: rapid detection, limited genetic diversity, and long-term clinical outcome in a local experience. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:1213–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gabus V, Grenak-Degoumois Z, Jeanneret S, Rakotoarimanana R, Greub G, Genne D. Tropheryma whipplei tricuspid endocarditis: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Reports. 2010;4:245. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kolek M, Zaloudikova B, Freiberger T, Brat R. Aortic and mitral valve infective endocarditis caused by Tropheryma whipplei and with no gastrointestinal manifestations of Whipple’s disease. Klin Mikrobiol Infekc Lek. 2007;13:213–6 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mallmann C, Siemoneit S, Schmiedel D, Petrich A, Gescher DM, Halle E, Fluorescence in situ hybridization to improve the diagnosis of endocarditis: a pilot study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:767–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miguelena J, Munoz R, Maseda R, Epeldegui A. Endocarditis due to Tropheryma whipplei. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2010;63:250–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Naegeli B, Bannwart F, Bertel O. An uncommon cause of recurrent strokes: Tropheryma whippelii endocarditis. Stroke. 2000;31:2002–3 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Voldstedlund M, Pedersen LN, Baandrup U, Fuursted K. Whipple’s disease—a cause of culture-negative endocarditis. Ugeskr Laeger. 2004;166:3731–2 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- West D, Hutcheon S, Kain R, Reid T, Walton S, Buchan K. Whipple’s endocarditis. J R Soc Med. 2005;98:362–4 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Whistance RN, Elfarouki GW, Vohra HA, Livesey SA. A case of Tropheryma whipplei infective endocarditis of the aortic and mitral valves in association with psoriatic arthritis and lumbar discitis. J Heart Valve Dis. 2011;20:353–6 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Williams OM, Nightingale AK, Hartley J. Whipple’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1479–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Love SM, Morrison L, Appleby C, Modi P. Tropheryma whipplei endocarditis without gastrointestinal involvement. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2012;15:161–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Greub G, Lepidi H, Rovery C, Casalta JP, Raoult D. Diagnosis of infectious endocarditis in patients undergoing valve surgery. Am J Med. 2005;118:230–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar