Volume 19, Number 2—February 2013
Dispatch
Macrolide- and Rifampin-Resistant Rhodococcus equi on a Horse Breeding Farm, Kentucky, USA
Figure 2
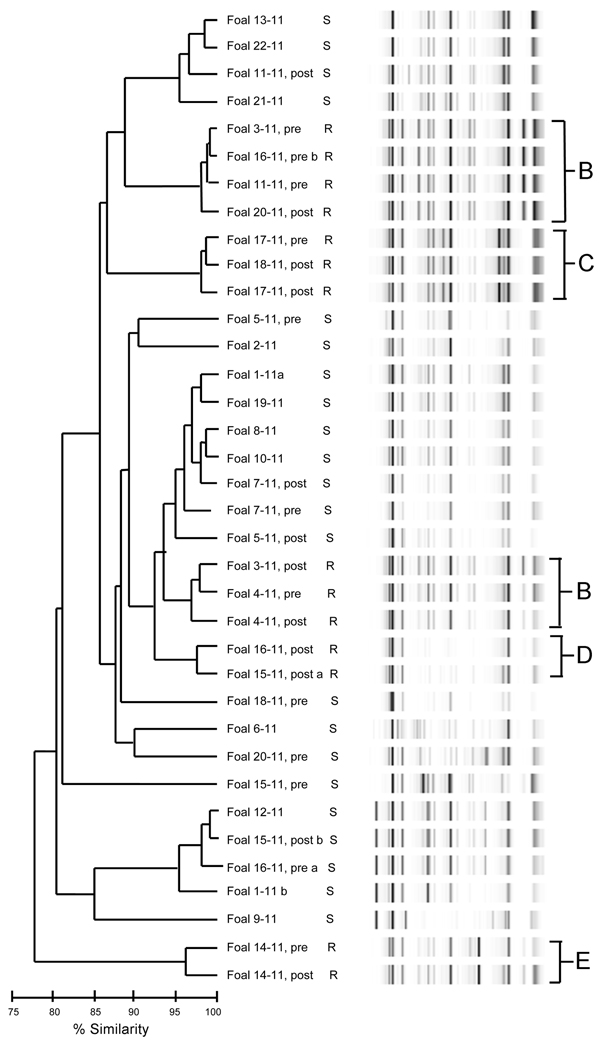
Figure 2. . Dendrogram and virtual gel repetitive sequence–based PCR fingerprint patterns of 36 Rhodococcus equi isolates obtained from foals on horse breeding farm, Kentucky, USA, 2011. Macrolide and rifampin susceptibility (S) and resistance (R) are indicated. B–E indicates clusters of drug-resistant isolates. Foals from which pretreatment (pre) and posttreatment (post) samples were obtained are indicated. a and b indicate samples from which 2 isolates were obtained.
1Current affiliation: Kalon Biotherapeutics LLC, College Station, Texas, USA.
Page created: January 22, 2013
Page updated: January 22, 2013
Page reviewed: January 22, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.