Volume 19, Number 3—March 2013
Research
Treatment Outcomes for Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis and HIV Co-infection
Figure 2
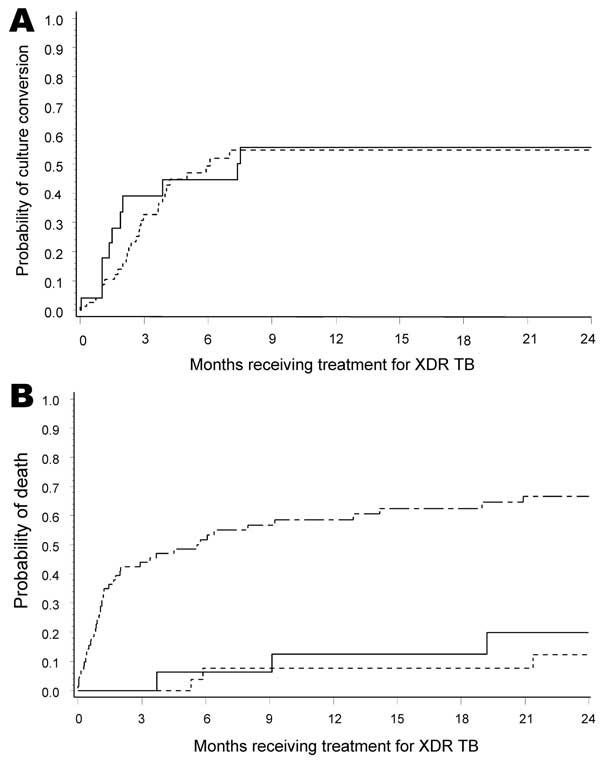
Figure 2. . A) Kaplan-Meier curves for sputum culture conversion for HIV-positive (dashed line) and HIV-negative (solid line) patients with extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR TB) receiving treatment, KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. Sputum culture conversion is defined as 2 consecutive monthly TB cultures with no growth after 6 weeks of incubation after initiation of treatment (p = 0.706). p value was adjusted for age, initial smear result, and HIV status. B) Kaplan-Meier curves for patients receiving treatment for XDR TB stratified by sputum culture conversion status (p<0.0001). Solid line indicates conversion ≤2 months after initiation of treatment, dashed line indicates conversion >2 months after initiation of treatment, and top line with small and large dashes indicates no conversion. p values were adjusted for sex, TB treatment history, and HIV status. There was no significant difference between patients who showed culture conversion <2 months and >2 months after initiation of treatment (p = 0.5182).