Volume 19, Number 3—March 2013
Research
Lack of Norovirus Replication and Histo-Blood Group Antigen Expression in 3-Dimensional Intestinal Epithelial Cells
Figure 2
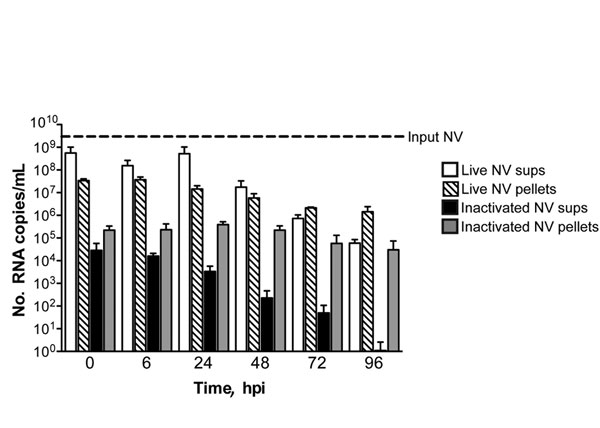
Figure 2. . . No evidence of productive Norwalk virus (NV) replication in 3-dimensional intestinal aggregates by quantitative reverse transcription PCR analysis. Supernatants (sups) and cell pellets were harvested for RNA at 0, 6, 24, 48, 72, and 96 hours postinoculation (hpi) with live and inactivated NV and analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription PCR. There was no significant increase (p>0.05) in NV RNA copy number over time in the supernatants or cell pellets relative to input virus. Error bars indicate SEM.
Page created: February 12, 2013
Page updated: February 12, 2013
Page reviewed: February 12, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.