Volume 19, Number 7—July 2013
Dispatch
Novel Bartonella Agent as Cause of Verruga Peruana
Figure 2
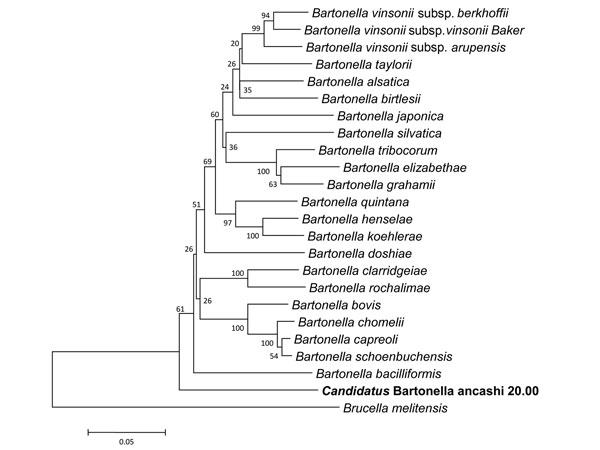
Figure 2. . Phylogeny for concatenated sequences of novel Bartonella isolate (boldface), including a 312-character fragment of gltA and a 589-character fragment of rpoB. The neighbor-joining tree method (1,000 bootstrap replicates) was employed using MEGA5 software (11), and the distances were calculated by using the Jukes-Cantor method, in which units are calculated as the number of base pair substitutions per site (10). Brucella melitensis was used as the outgroup.
References
- Schultz MG. A history of bartonellosis (Carrion’s disease). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968;17:503–15 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maguina C, Garcia PJ, Gotuzzo E, Cordero L, Spach DH. Bartonellosis (Carrion’s disease) in the modern era. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:772–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chamberlin J, Laughlin LW, Romero S, Solórzano N, Gordon S, Andre RG, Epidemiology of endemic Bartonella bacilliformis: a prospective cohort study in a Peruvian mountain valley community. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:983–90 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Eremeeva ME, Gerns HL, Lydy SL, Goo JS, Ryan ET, Mathew SS, Bacteremia, fever, and splenomegaly caused by a newly recognized Bartonella species. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2381–7 and. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mallqui V, Speelmon EC, Verástegui M, Maguiña-Vargas C, Pinell-Sallis P, Sonicated diagnostic immunoblot for bartonellosis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2000;7:1–5 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Walker TS, Winkler HH. Bartonella bacilliformis: colonial types and erythrocyte adherence. Infect Immun. 1981;31:480–6 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maass M, Schreiber M, Knobloch J. Detection of Bartonella bacilliformis in cultures, blood, and formalin preserved skin biopsies by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Trop Med Parasitol. 1992;43:191–4 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rolain JM, Brouqui P, Koehler JE, Maguina C, Dolan MJ, Raoult D. Recommendations for treatment of human infections caused by Bartonella species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:1921–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Arroyo A. Treatment outlines for non-complicated Carrion’s disease, in Caraz, Peru. Anales de la Facultad de Medecina. 2008;69:7–11.
- Maass M, Schreiber M, Knobloch J. Detection of Bartonella bacilliformis in cultures, blood, and formalin preserved skin biopsies by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Trop Med Parasitol. 1992;43:191–4 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zeaiter Z, Liang Z, Raoult D. Genetic classification and differentiation of Bartonella species based on comparison of partial ftsZ gene sequence. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:3641–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- La Scola B, Zeaiter Z, Khamis A, Raoult D. Gene-sequence-based criteria for species definition in bacteriology: the Bartonella paradigm. Trends Microbiol. 2003;11:318–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jones KE, Patel NG, Levy MA, Storeygard A, Balk D, Gittleman JL, Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature. 2008;451:990–3 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sanchez Clemente N, Ugarte-Gil CA, Solórzano N, Maguiña C, Pachas P, Bartonella bacilliformis: a systematic review of the literature to guide the research agenda for elimination. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6:e1819.
Page created: June 18, 2013
Page updated: June 18, 2013
Page reviewed: June 18, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.