Volume 19, Number 7—July 2013
Letter
Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus, Zealand, Denmark, 2011
Figure
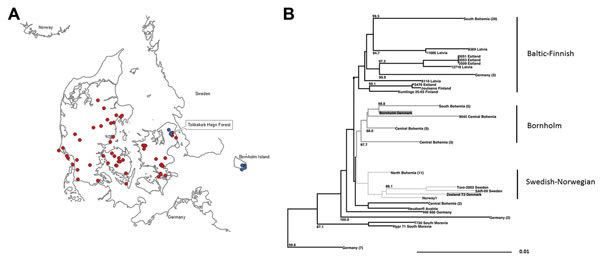
Figure. . . A) Tick collection areas in Denmark. Red indicates ticks sampled from animals; blue indicates flagging. B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic analysis of a 1,488-nt set of 78 tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV)–Eur E gene sequences including reference strains Neudoerfl (Austria) and Hypr 71 (South Moravia) performed in ClustalW with a 1,000 bootstrap approach (LASERGENE, MEGALIGN, DENDROSCOPE) outgrouped to Louping ill virus (data not shown). Sequence designations of central European strains as in (8). Dark gray indicates Denmark Bornholm clade; light gray indicates Swedish-Norwegian clade. For simplicity, some subtrees were collapsed; these are designated with region and number of sequences in the collapsed subtree in brackets.
References
- Jääskeläinen AE, Tonteri E, Sironen T, Pakarinen L, Vaheri A, Vapalahti O. European subtype tick-borne encephalitis virus in Ixodes persulcatus ticks. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:323–5 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Skarphédinsson S, Jensen PM, Kristiansen K. Survey of tick-borne infections in Denmark. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:1055–61 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Randolph SE, Rogers DJ. Fragile transmission cycles of tick-borne encephalitis virus may be disrupted by predicted climate change. Proc Biol Sci. 2000;267:1741–4 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fomsgaard A, Christiansen CB, Bødker R. First identification of tick-borne encephalitis in Denmark outside of Bornholm, August 2009. Euro Surveill. 2009;14:pii19326 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schwaiger M, Cassinotti P. Development of a quantitative real-time RT-PCR assay with internal control for the laboratory detection of tick borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) RNA. J Clin Virol. 2003;27:136–45 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fertner ME, Mølbak L, Boye Pihl TP, Fomsgaard A, Bødker R. First detection of tick borne “Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis” in Denmark 2011. Euro Surveill. 2012;17:pii20096 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sonenshine DE. Biology of ticks. Vol. 2. New York: Oxford University Press; 1993.
- Weidmann M, Ruzek D, Krivanec K, Zöller G, Essbauer S, Pfeffer M, Relation of genetic phylogeny and geographical distance of tick-borne encephalitis virus in central Europe. J Gen Virol. 2011;92:1906–16 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Melik W, Nilsson AS, Johansson M. Detection strategies of tick-borne encephalitis in Swedish Ixodes ricinus reveal evolutionary characteristics of emerging tick-borne flavivirus. Arch Virol. 2007;152:1027–34 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jaenson TGT, Hjertqvist M, Bergström T, Lundkvist A. Why is tick-borne encephalitis increasing? A review of the key factors causing the increasing incidence of human TBE in Sweden. Parasit Vectors. 2012;5:184.
Page created: June 11, 2013
Page updated: June 11, 2013
Page reviewed: June 11, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.